Difference between revisions of "YFL064C"
(→Community Commentary) |
|||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
[[File:pH-YFL064C.PNG]] | [[File:pH-YFL064C.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Cold Shock Sensitivity=== | ||
| + | [[File:YFL064CBB.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Protocol: [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/UW-Stout/Cold_Shock Cold Shock] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
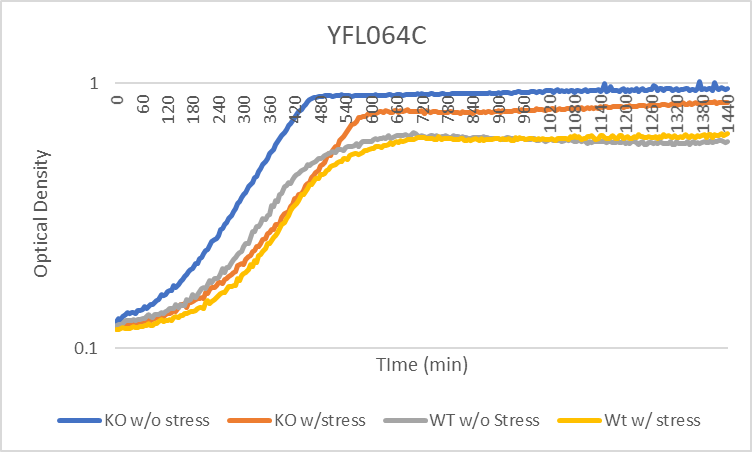
| + | YFL064C is neither more or less sensitive to the cold than the wild type strain. This is shown because the doubling times change the same amount before and after the cold shock in both the wild type strain and YFL064C. | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
<!-- REFERENCES ARE AUTOMATICALLY GENERATED. PLEASE DON'T EDIT THIS SECTION--> | <!-- REFERENCES ARE AUTOMATICALLY GENERATED. PLEASE DON'T EDIT THIS SECTION--> | ||
{{RefHelp}} | {{RefHelp}} | ||
Latest revision as of 18:50, 9 May 2019
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry!
| Systematic name | YFL064C |
| Gene name | |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr VI:3846..3322 |
| Primary SGDID | S000001830 |
Description of YFL064C: Putative protein of unknown function[1]
Contents
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
This gene is part of the UW-Stout Orphan Gene Project. Learn more here.
UW-Stout/Sensitivity To Nitrogen Starvation
Knocking out the YFL064C seems to have no effect on growth after incubating for 5 days on the Nitrogen omitted media.
Ultraviolet Sensitivity
YFL064C is more sensitive than BY4735(wild) given that there is less colonizes present when under the same stress.
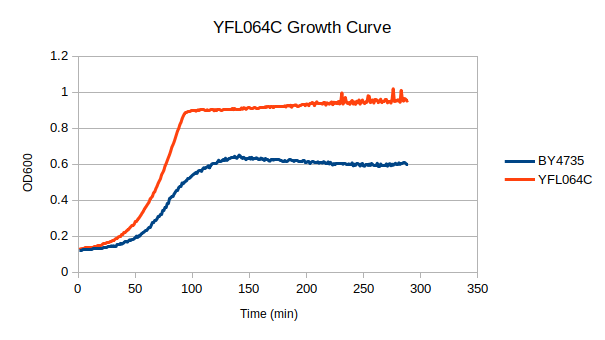
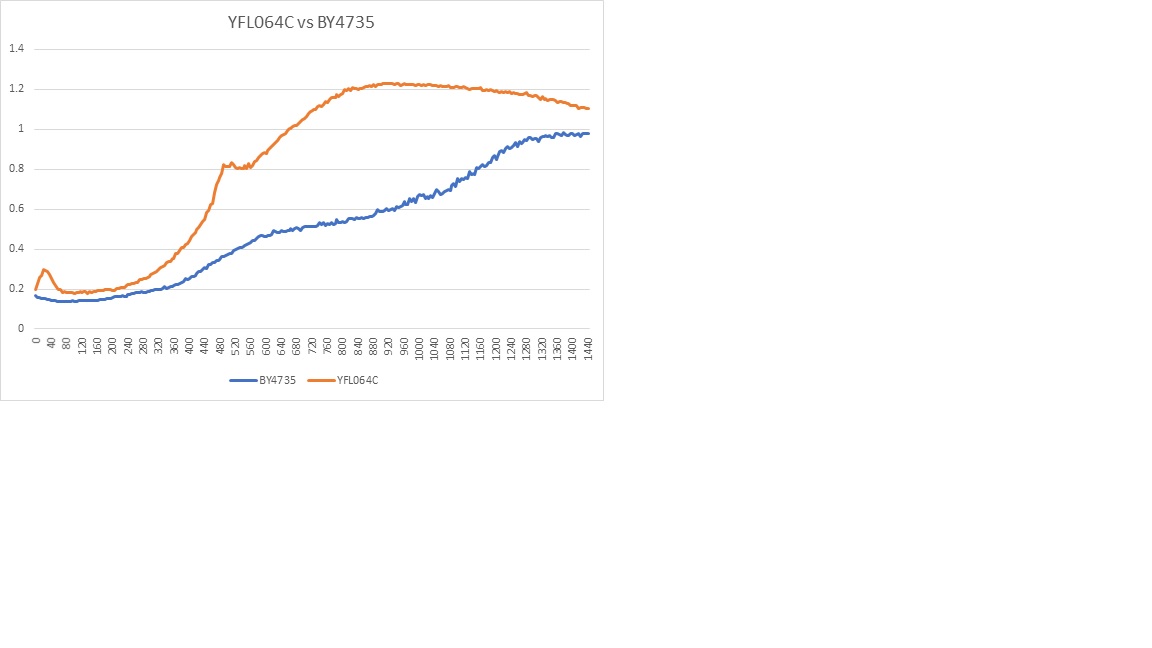
Growth Curve
In a BY4735 background, knocking out YFL064C seems to have no effect on growth rate in log-phase. In this assay, the BY4735 strain's doubling time was 124 minutes, and the YFL064C knock-out strain's doubling time was also 124 minutes. However, the knock-out strain did reach a substantially higher OD600 before saturating.
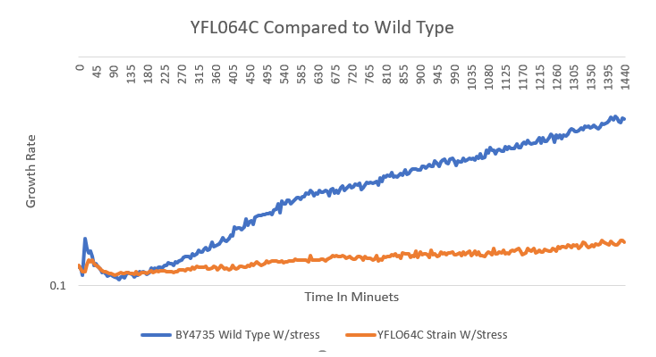
G-418 Stress
In the BY4735 background, knocking out the YFL064C strain seem to have a different kind of effect, where the YFL064C growth was slowed down but grew faster than the BY4735. In the knock-out experiment, the BY4735 strain's doubling time was 149 minutes, whereas the YFL064C knock-out strain's doubling time was 142 minutes. In the calibration experiment, the BY4735 strain's doubling time was 64 minutes, whereas the YFL064C knock-out strain's doubling time was 100 minutes.
Methanol Sensitivity
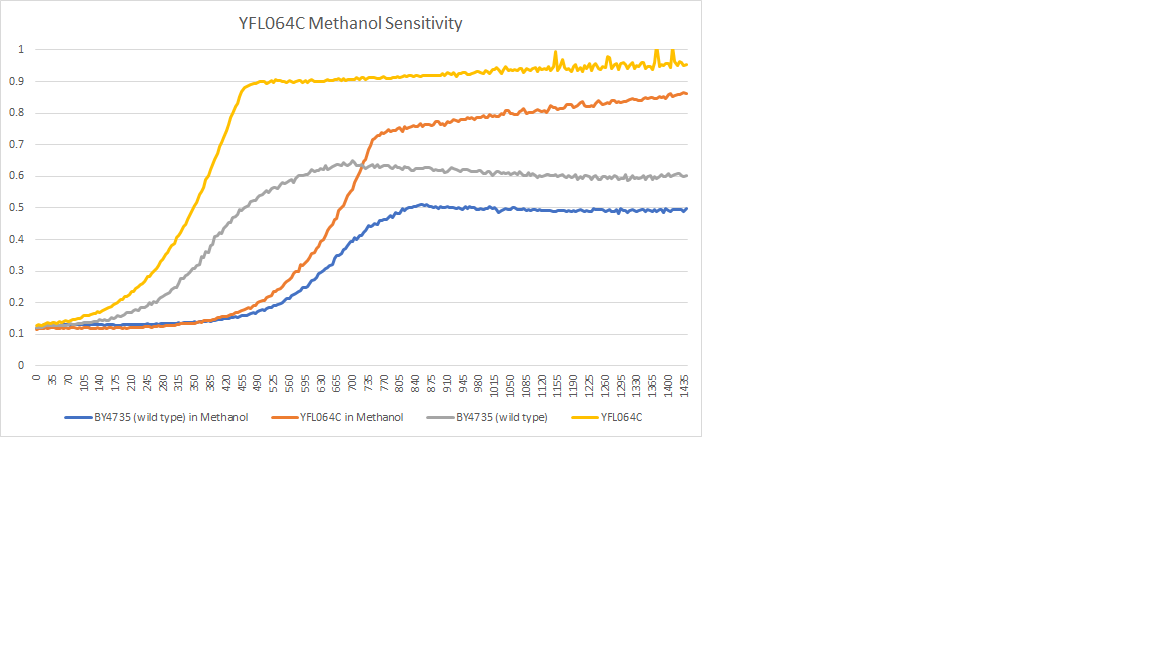
The wild type had a doubling time of 200 min, the YFL064c had a doubling time of 170 min. The methanol had little to no effect on these strains.
Heat Shock
Heat shock had no change on the doubling time, but the starting amount of yeast cells less. The heat seemed to kill off the cells, the longer they were in the hot water bath.
Stressing with Hydroxyurea
Hydroxyurea Protocol -The wild type strain had only a small difference in doubling time when stressed with Hydroxyurea;YFL064C had about a 10 minute difference of doubling time when stressed with hydroxyurea, indicating that this gene strain most likely does not play a vital role in DNA replication.
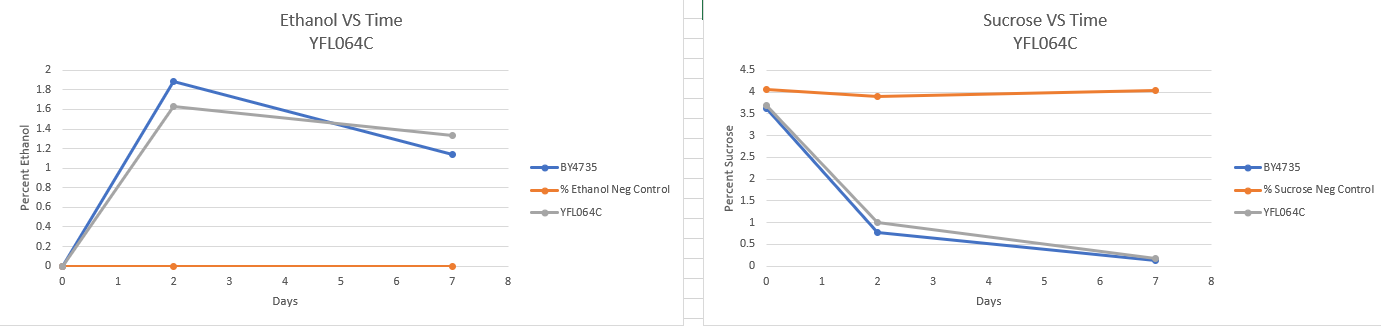
Fermentation
Fermentation protocol link [2] - There appears to be no major difference in fermentation rate. The lower final ethanol percentage could be a result of evaporation. If this experiment were to be carried out again then it should be done in an air tight container.
Caffeine Sensitivity
Protocol above, results show very different initial reactions, pace of growth very different, but ended at about the same pace.
Stressing with pH
pH stress protocol link [3]
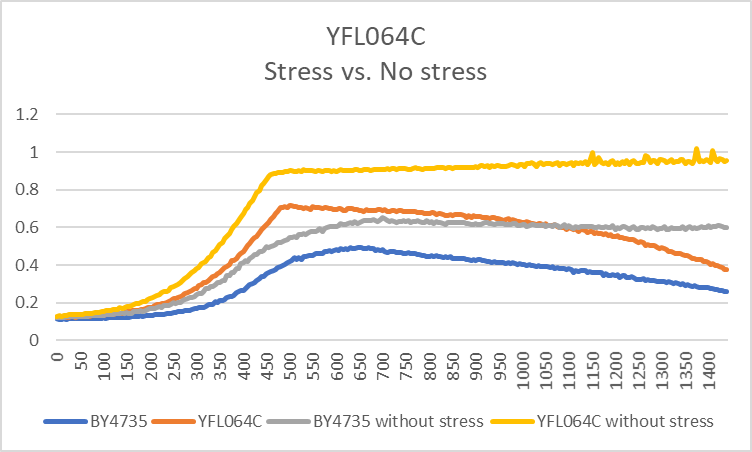
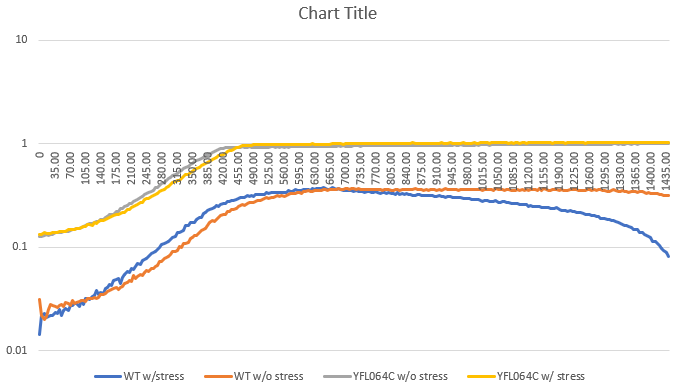
The wild type strain had a significant difference compared to the yeast strain YFL064C and when we stressed it out at the pH of 4. It displayed that it was more resilient to this particular pH and grew happily than the YFL064C yeast strain did.
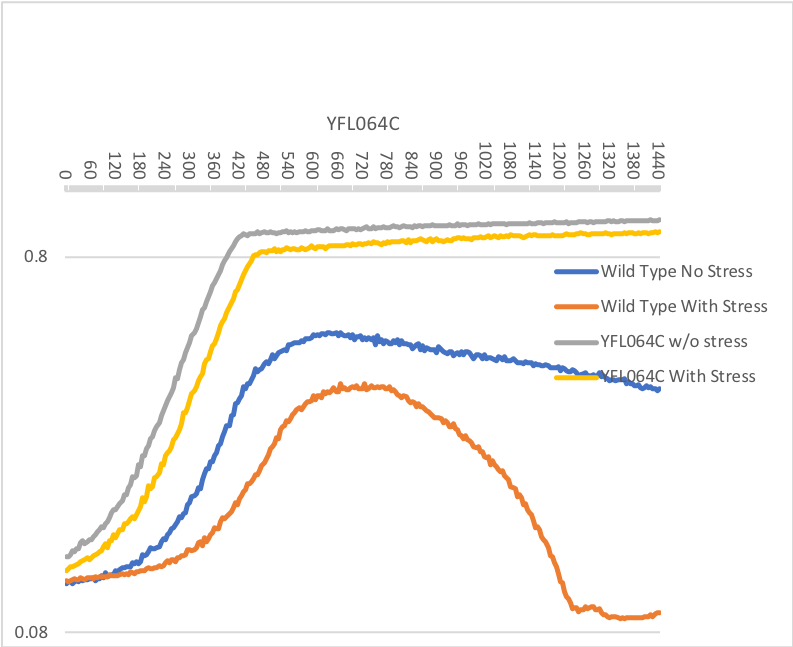
Cold Shock Sensitivity
Protocol: Cold Shock
YFL064C is neither more or less sensitive to the cold than the wild type strain. This is shown because the doubling times change the same amount before and after the cold shock in both the wild type strain and YFL064C.
References
See Help:References on how to add references
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category