YLR426W
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry! <protect>
| Systematic name | YLR426W |
| Gene name | TDA5 |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr XII:987062..988113 |
| Primary SGDID | S000004418 |
Description of YLR426W: Putative protein of unknown function; detected in highly purified mitochondria in high-throughput studies; proposed to be involved in resistance to mechlorethamine and streptozotocin; null mutant sensitive to expression of top1-T722A allele[1][2][3][4]
</protect>
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
This gene is part of the UW-Stout Orphan Gene Project. Learn more here.
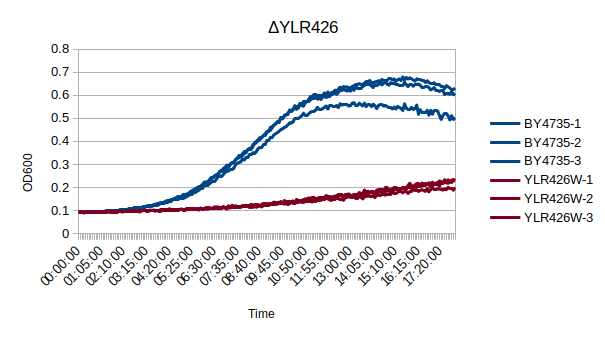
Growth Curve
In a BY4735 background, knocking out YLR426W seems to have a substantial effect on the strain's growth in complete media. In this assay, the BY4735 strain's doubling time was 162 minutes, while the YLR426W knock-out strain's doubling time was 660 minutes. (These doubling times are the means of three experiments.)
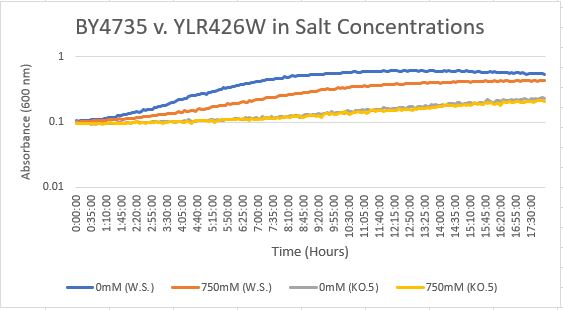
Salt Concentration (NaCl)
0mM NaCl conc. BY4735 strain's doubling time: 169 minutes
0mM NaCl conc. YLR426W strain's doubling time: 481 minutes
750mM NaCl conc. BY4735 strain's doubling time: 294 minutes
750mM NaCl conc. YLR426W strain's doubling time: 909 minutes
The graph above shows the growth rate for the previously listed strains and the relative level of NaCl concentration. Comparing the YLR426W doubling times between 0mM and 750mM NaCl, there is a tremendous effect on the growth rate. This effect negatively influences the knockout strain's (YLR426W) growth rate.
<protect>
References
See Help:References on how to add references
- ↑ Lee W, et al. (2005) Genome-wide requirements for resistance to functionally distinct DNA-damaging agents. PLoS Genet 1(2):e24 SGD PMID 16121259
- ↑ Reid RJ, et al. (2011) Selective ploidy ablation, a high-throughput plasmid transfer protocol, identifies new genes affecting topoisomerase I-induced DNA damage. Genome Res 21(3):477-86 SGD PMID 21173034
- ↑ Reinders J, et al. (2006) Toward the complete yeast mitochondrial proteome: multidimensional separation techniques for mitochondrial proteomics. J Proteome Res 5(7):1543-54 SGD PMID 16823961
- ↑ Sickmann A, et al. (2003) The proteome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(23):13207-12 SGD PMID 14576278
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>