YBL113C
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry! <protect>
| Systematic name | YBL113C |
| Gene name | |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr II:2658..280 |
| Primary SGDID | S000002153 |
Description of YBL113C: Helicase-like protein encoded within the telomeric Y' element[1]
</protect>
Contents
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
This gene is part of the UW-Stout Orphan Gene Project. Learn more here.
UW Stout/D2O SP22
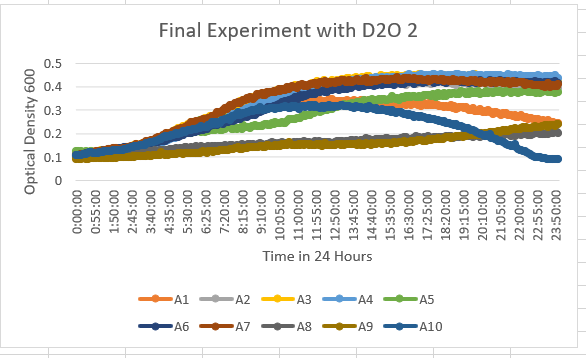
In the results of the 35% dilution of D2O with the Knock-out Yeast Strain YBL113C (A9) we can see that the growth curve stayed in the 0.1-0.3 range throughout the data collected in 24 hours. This tells us it was more sensitive to the dilution of D2O.
UW-Stout/Heat Shock SP22
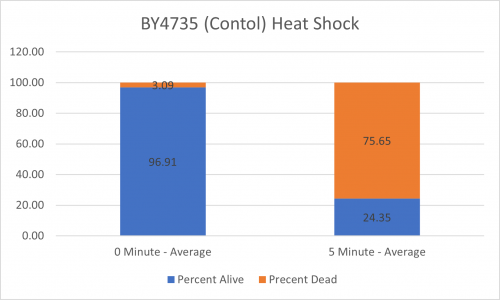
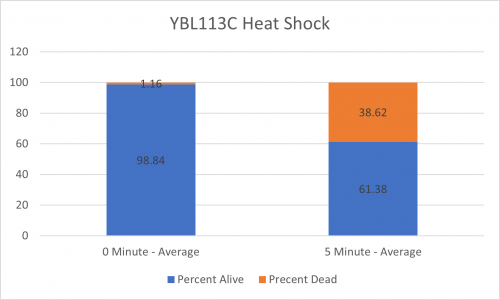
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to heat shock.
Results
Interpretation
From the data gathered, there was a medium positive effect to knocking out this gene when it came to the yeast's ability to hold up to heat shock. The modified yeast cells were 252% more resistant to heat shock than the control.
UW Stout/Sucrose Fermentation SP22
| Gene | Glucose | Fructose | Ethanol |
| Standard solution | 2.0000 | 0.2000 | 2.0000 |
| YDl109C | 0.3800 | 0.3933 | 0.3430 |
| YGL140C | 0.2212 | 0.2685 | 0.1867 |
| YOR111W | 0.3332 | 0.3598 | 0.1343 |
| YHL029C | 0.3870 | 0.2368 | 0.1151 |
| YDR307W | 0.4366 | 0.2487 | 0.0606 |
| YNL058C | 0.2710 | 0.3056 | 0.1577 |
| YCL049C | |||
| YGR079W | |||
| YBL113C | 0.3498 | 0.2012 | 0.1434 |
| BY4735 | 0.3171 | 0.3084 | 0.3541 |
Interpretation
This gene produced 40.50% of the amount of ethanol that the wild type produced.
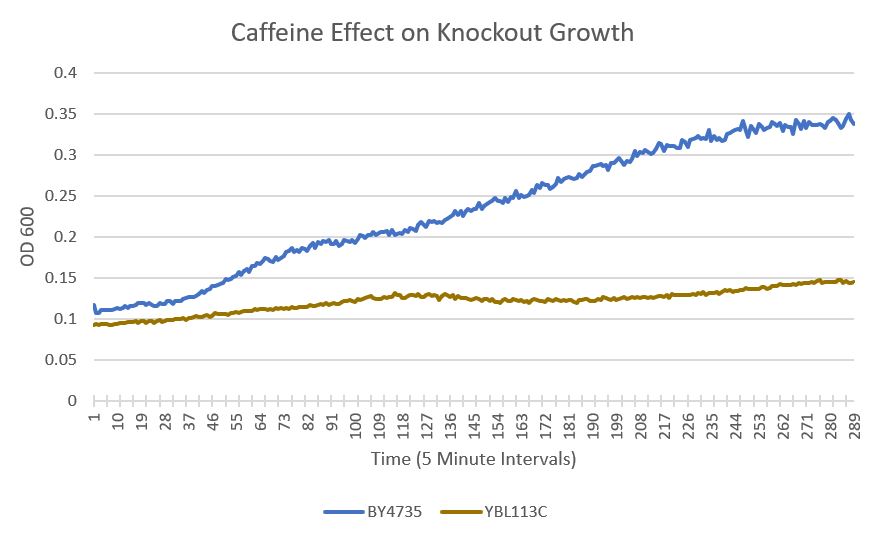
UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to 4mM of caffeine.
Results
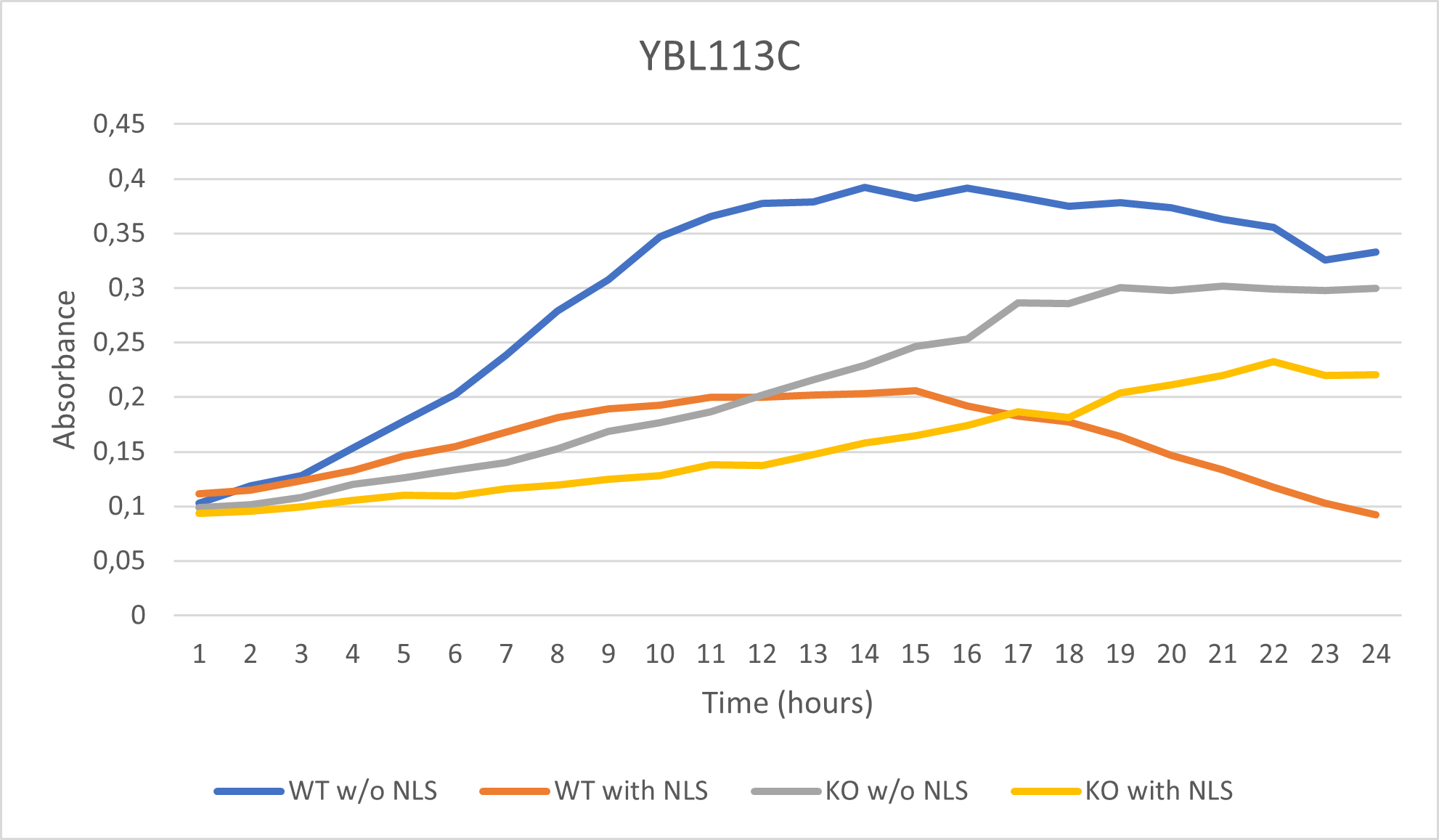
- BY4735(wild type yeast) and YBL113C(knockout yeast gene) growth after being subjected to 4mM caffeine solution.
Interpretation
<protect>
References
See Help:References on how to add references
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>