Difference between revisions of "YGR079W"
(→Interpretation) |
(→Results) |
||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
====Results==== | ====Results==== | ||
| − | :BY4735(wild type yeast) and YGR079W(knockout yeast gene) growth after being subjected to 4mM caffeine solution. | + | :BY4735(wild type yeast) and YGR079W(knockout yeast gene) growth after being subjected to 4mM caffeine solution [[UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22|following this protocol]]. |
| − | [[Image:YGR079W.jpeg]] | + | [[Image:YGR079W.jpeg|500px]] |
| + | ===Interpretation=== | ||
| + | As seen in the growth chart, YGR079W has a much slower rate of growth when compared to the Wild-Type yeast. | ||
====Interpretation==== | ====Interpretation==== | ||
Revision as of 15:30, 5 May 2022
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry! <protect>
| Systematic name | YGR079W |
| Gene name | |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr VII:640720..641832 |
| Primary SGDID | S000003311 |
Description of YGR079W: Putative protein of unknown function; YGR079W is not an essential gene[1]
</protect>
Contents
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
DNA and RNA Details
Other DNA and RNA Details
Other Topic: expression
Specifically higher expression in phosphorus limited chemostat cultures versus phosphorus excess. [2] [3]
This gene is part of the UW-Stout Orphan Gene Project. Learn more here.
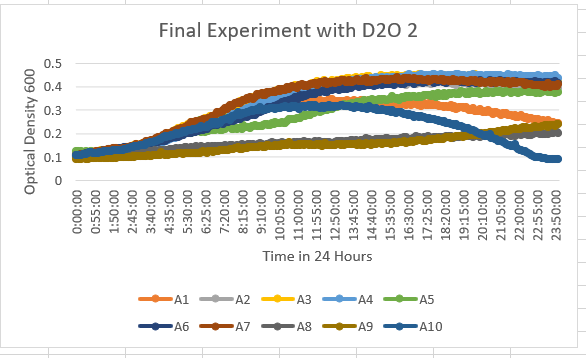
UW Stout/D2O SP22
The Knock Out Yeast Strain YGR079W (A8) Is more of a resistant strain to the 35% dilution of D20. With the range of maximum OD being about 0.2-0.3 OD 600. However, the growth of this is also a slower growth rate.
UW Stout/Sucrose Fermentation SP22
| Gene | Glucose | Fructose | Ethanol |
| Standard solution | 2.0000 | 0.2000 | 2.0000 |
| YDl109C | 0.3800 | 0.3933 | 0.3430 |
| YGL140C | 0.2212 | 0.2685 | 0.1867 |
| YOR111W | 0.3332 | 0.3598 | 0.1343 |
| YHL029C | 0.3870 | 0.2368 | 0.1151 |
| YDR307W | 0.4366 | 0.2487 | 0.0606 |
| YNL058C | 0.2710 | 0.3056 | 0.1577 |
| YCL049C | 0.4078 | 0.3052 | 0.1969 |
| YGR079W | 0.4042 | 0.1589 | 0.0080 |
| YBL113C | 0.3498 | 0.2012 | 0.1434 |
| BY4735 | 0.3171 | 0.3084 | 0.3541 |
Interpretation
This gene produced 2.26% of the amount of ethanol that the wild type produced. There is a high probability that this gene affects fermentation since there is such a low amount of ethanol produced but further tests are required.
<protect>
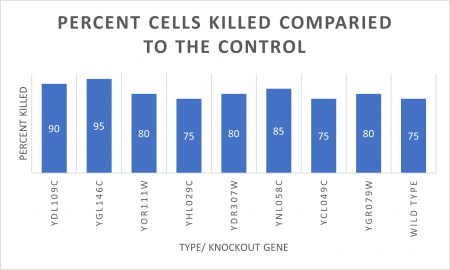
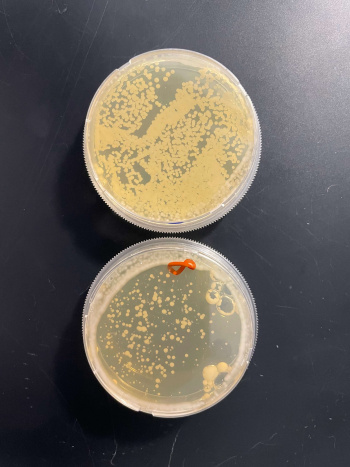
UW-Stout/UV Light SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested under a UV Light using this protocol.
RESULTS
INTERPERTATION
In the graph and photos above, exposing this gene to 600 seconds of 400 Watt UV Light killed approximately 80% of yeast cell cultures, compared to its control counterpart, which was the same gene and amount of cells, just was not exposed to UV Light.
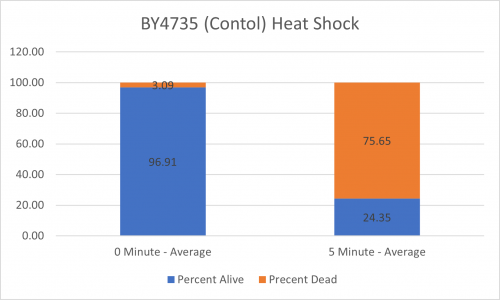
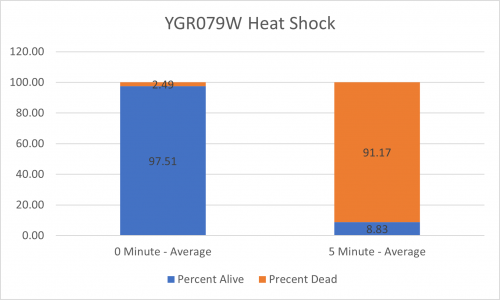
UW-Stout/Heat Shock SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to heat shock.
Results
Interpretation
From the data gathered, there was a medium negative effect to knocking out this gene when it came to the yeast's ability to hold up to heat shock. The modified yeast cells were only 36% as resistant to heat shock than the control.
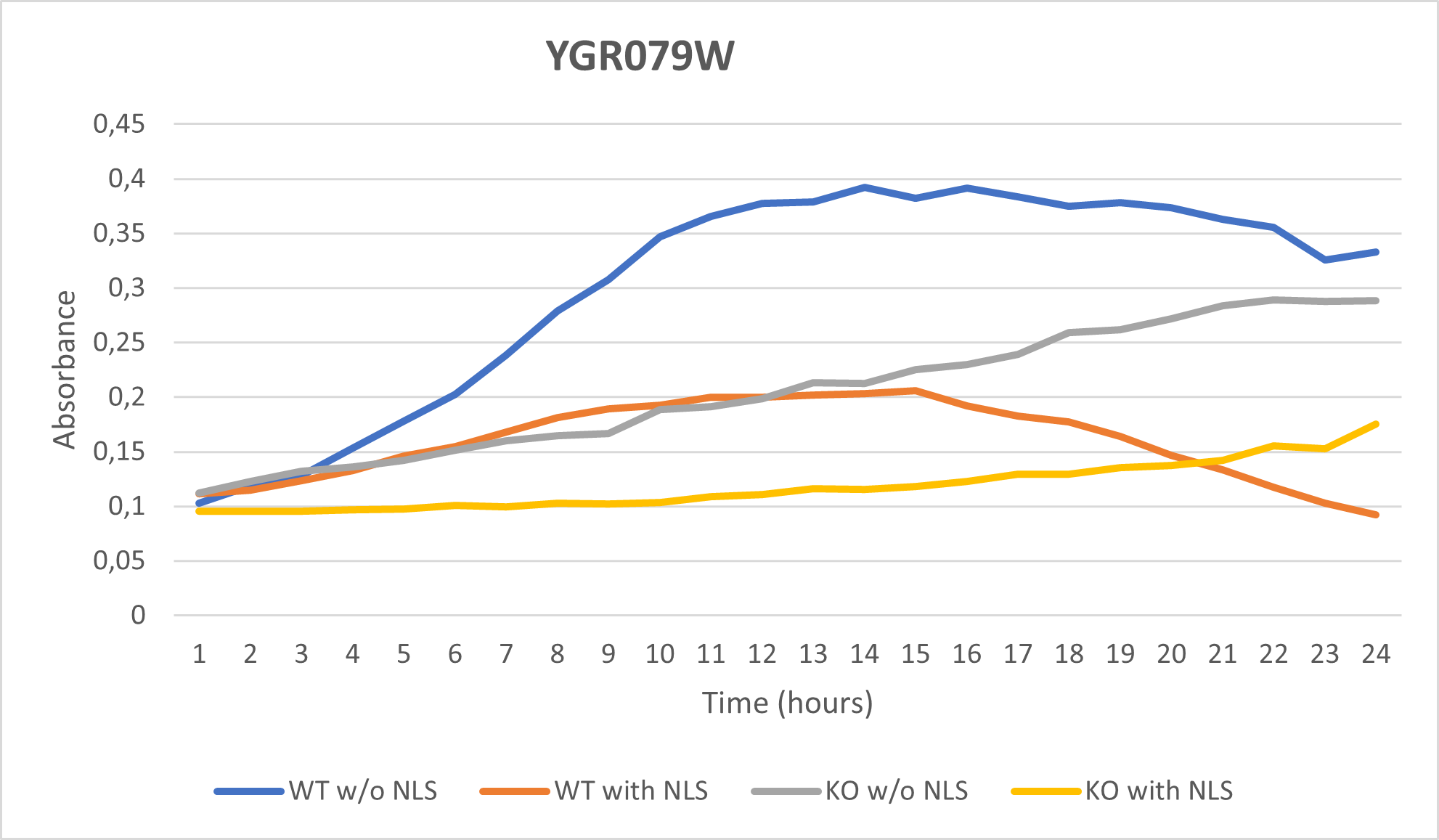
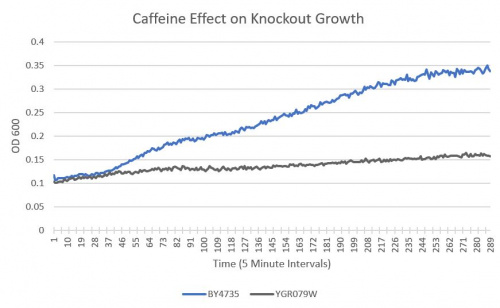
UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to 4mM of caffeine.
Results
- BY4735(wild type yeast) and YGR079W(knockout yeast gene) growth after being subjected to 4mM caffeine solution following this protocol.
===Interpretation===
As seen in the growth chart, YGR079W has a much slower rate of growth when compared to the Wild-Type yeast.
Interpretation
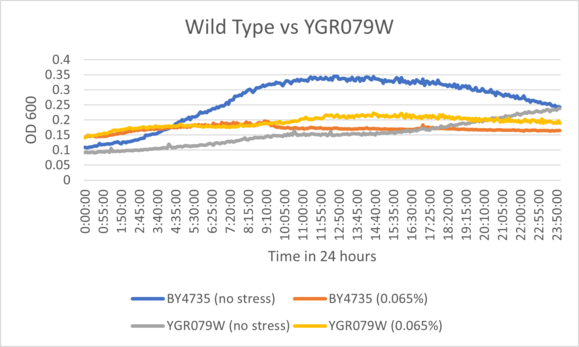
UW-Stout/Hydrogen Peroxide SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to hydrogen peroxide.
Results
BY4735 and YGR079W after being exposed to 0.065% dilution of hydrogen peroxide solution.
Interpretation
Based on the growth curve, YGR079W demonstrated close to standard inhibition under the stress of the hydrogen peroxide solution when compared to wild type cells. It's control exhibited slow growth but ended around the same value as wild type cells.
References
See Help:References on how to add references
- ↑ Giaever G, et al. (2002) Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 418(6896):387-91 SGD PMID 12140549
- ↑ Boer VM, et al. (2003) The genome-wide transcriptional responses of Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown on glucose in aerobic chemostat cultures limited for carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, or sulfur. J Biol Chem 278(5):3265-74 SGD PMID 12414795
- ↑ submitted by Viktor Boer on 2003-07-25
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>