Difference between revisions of "YHL029C"
(→Interpretation) |
(→UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22) |
||
| Line 140: | Line 140: | ||
===[[UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22]]=== | ===[[UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22]]=== | ||
| − | As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout [[UW-Stout/About|Orphan Gene Project]] this gene was tested by exposing the cells to 4mM of caffeine. | + | As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout [[UW-Stout/About|Orphan Gene Project]] this gene was tested by exposing the cells to 4mM of caffeine [[UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22|following this protocol]]. |
====Results==== | ====Results==== | ||
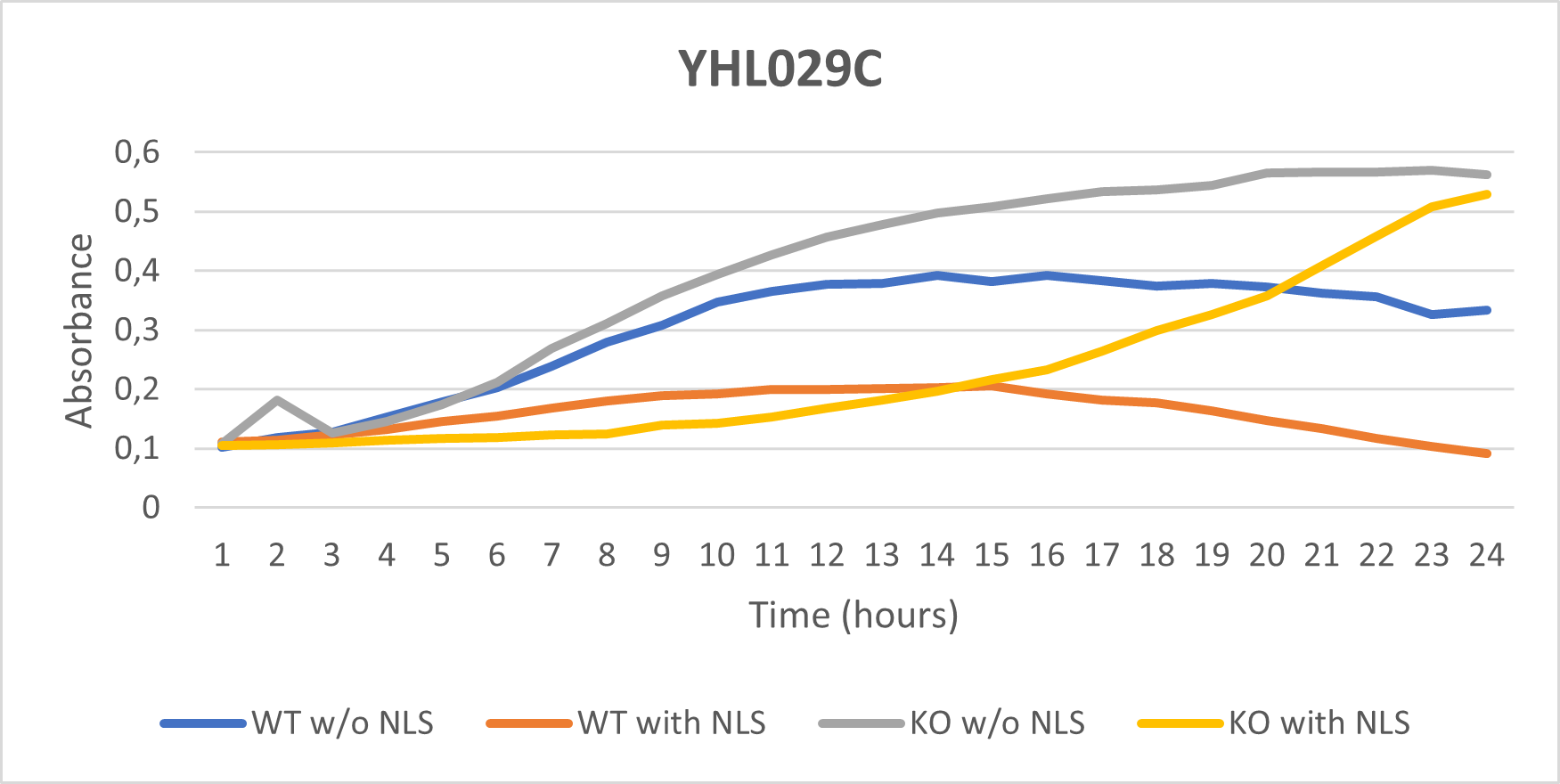
:BY4735(wild type yeast) and YHL029C(knockout yeast gene) growth after being subjected to 4mM caffeine solution. | :BY4735(wild type yeast) and YHL029C(knockout yeast gene) growth after being subjected to 4mM caffeine solution. | ||
| − | [[Image:YHL029C.jpeg]] | + | [[Image:YHL029C.jpeg|500px]] |
====Interpretation==== | ====Interpretation==== | ||
| − | + | As seen in the growth curve, YHL029C is more growth resistant to caffeine than the Wild-Type yeast. This is measurable as a 35% difference in Optical Density 600. | |
===[[UW-Stout/Hydrogen Peroxide SP22]]=== | ===[[UW-Stout/Hydrogen Peroxide SP22]]=== | ||
Revision as of 15:17, 5 May 2022
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry! <protect>
| Systematic name | YHL029C |
| Gene name | OCA5 |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr VIII:47968..45929 |
| Primary SGDID | S000001021 |
Description of YHL029C: Cytoplasmic protein required for replication of Brome mosaic virus in S. cerevisiae, which is a model system for studying replication of positive-strand RNA viruses in their natural hosts[1][2]
</protect>
Contents
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
This gene is part of the UW-Stout Orphan Gene Project. Learn more here.
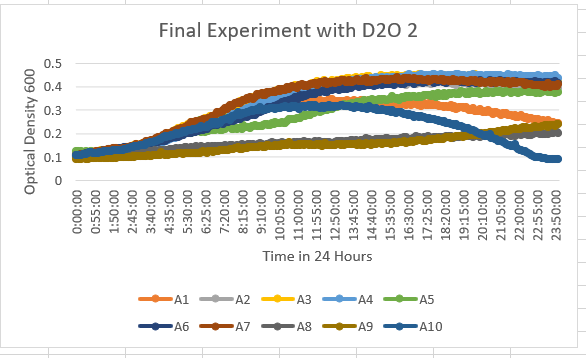
UW Stout/D2O SP 22
The YHL029C Knock Out Yeast Strain (A4) is unaffected by the 35% dilution D2O . With the maximum optical density of about 0.5-0.6 OD 600.
UW Stout/Sucrose Fermentation SP22
| Gene | Glucose | Fructose | Ethanol |
| Standard solution | 2.0000 | 0.2000 | 2.0000 |
| YDl109C | 0.3800 | 0.3933 | 0.3430 |
| YGL140C | 0.2212 | 0.2685 | 0.1867 |
| YOR111W | 0.3332 | 0.3598 | 0.1343 |
| YHL029C | 0.3870 | 0.2368 | 0.1151 |
| YDR307W | 0.4366 | 0.2487 | 0.0606 |
| YNL058C | 0.2710 | 0.3056 | 0.1577 |
| YCL049C | 0.4078 | 0.3052 | 0.1969 |
| YGR079W | 0.4042 | 0.1589 | 0.0080 |
| YBL113C | 0.3498 | 0.2012 | 0.1434 |
| BY4735 | 0.3171 | 0.3084 | 0.3541 |
Interpretation
This gene produced 32.50% of the amount of ethanol that the wild type produced.
<protect>
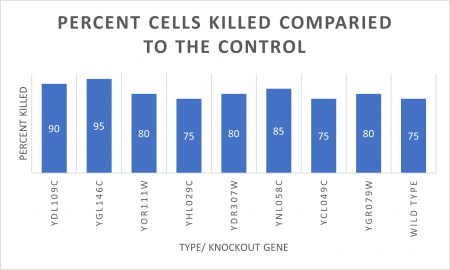
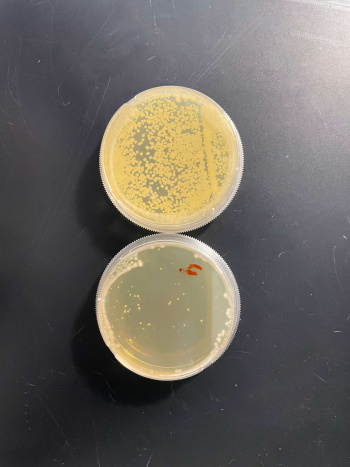
UW-Stout/UV Light SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested under a UV Light using this protocol.
RESULTS
INTERPERTATION
In the graph and photos above, exposing this gene to 600 seconds of 400 Watt UV Light killed approximately 75% of yeast cell cultures, compared to its control counterpart, which was the same gene and amount of cells, just was not exposed to UV Light.
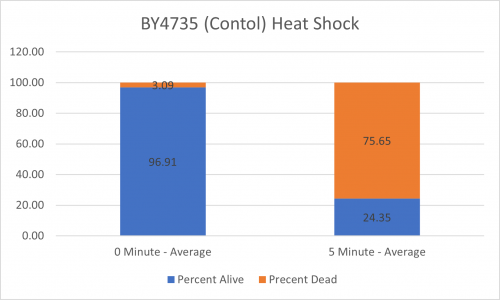
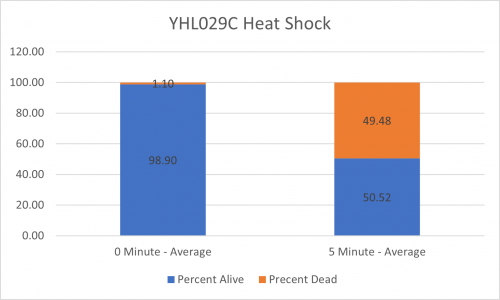
UW-Stout/Heat Shock SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to heat shock.
Results
Interpretation
From the data gathered, there was a medium positive effect to knocking out this gene when it came to the yeast's ability to hold up to heat shock. The modified yeast cells were 207% more resistant to heat shock than the control.
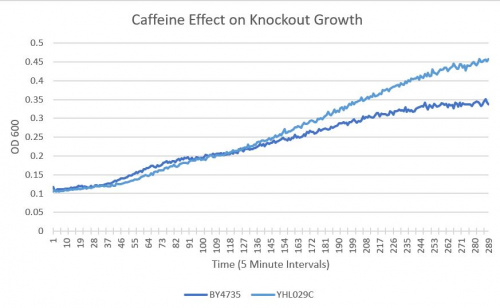
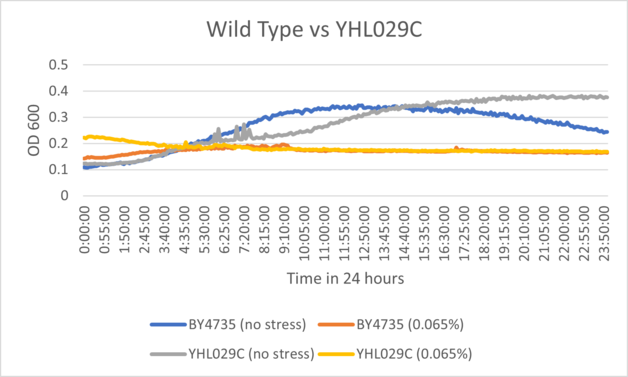
UW-Stout/Caffeine SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to 4mM of caffeine following this protocol.
Results
- BY4735(wild type yeast) and YHL029C(knockout yeast gene) growth after being subjected to 4mM caffeine solution.
Interpretation
As seen in the growth curve, YHL029C is more growth resistant to caffeine than the Wild-Type yeast. This is measurable as a 35% difference in Optical Density 600.
UW-Stout/Hydrogen Peroxide SP22
As part of the University of Wisconsin Stout Orphan Gene Project this gene was tested by exposing the cells to hydrogen peroxide.
Results
BY4735 and YHL029C after being exposed to 0.065% dilution of hydrogen peroxide solution.
Interpretation
Based on the growth curve, YHL029C displayed inhibition extremely identical to wild type yeast cells, and the range for both controls had a strong correlation. This suggests that the knockout may have had very little affect on oxidative stress response.
References
See Help:References on how to add references
- ↑ Huh WK, et al. (2003) Global analysis of protein localization in budding yeast. Nature 425(6959):686-91 SGD PMID 14562095
- ↑ Kushner DB, et al. (2003) Systematic, genome-wide identification of host genes affecting replication of a positive-strand RNA virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(26):15764-9 SGD PMID 14671320
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>