Difference between revisions of "YBR284W"
(→Community Commentary) |
(→Community Commentary) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
===[[UW-Stout/Bud Scars FA21]]=== | ===[[UW-Stout/Bud Scars FA21]]=== | ||
| − | Cells grown with this gene (YBR284W) knocked out had an average of 1.18 bud scars per cell while the wild type (BY-RY4735) had 0.85 bud scars per cell. Of 114 | + | Cells grown with this gene (YBR284W) knocked out had an average of 1.18 bud scars per cell while the wild type (BY-RY4735) had 0.85 bud scars per cell. Of 114 YBR284W cells counted, 135 bud scars were seen. This indicated that the YBR284W gene slows reproduction rate and thus bud scarring in yeast cells. |
<!-- PLEASE ADD Community Commentary ABOVE THIS MESSAGE. See below for an example of community annotation --> | <!-- PLEASE ADD Community Commentary ABOVE THIS MESSAGE. See below for an example of community annotation --> | ||
Revision as of 13:23, 14 December 2021
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry! <protect>
| Systematic name | YBR284W |
| Gene name | |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr II:771239..773632 |
| Primary SGDID | S000000488 |
Description of YBR284W: Protein of unknown function; some similarity to AMP deaminases but lacks key catalytic residues and does not rescue purine nucleotide metabolic defect of quadruple aah1 ade8 amd1 his1 mutant; null mutant exhibits longer telomeres, altered Ty mobility, decreased resistance to rapamycin and wortmannin, and synthetic phenotype with expression of alpha-synuclein; induced in response to hydrostatic pressure; not an essential gene[1][2][3][4][5][6][7]
</protect>
Contents
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
This gene is part of the UW-Stout Orphan Gene Project. Learn more here.
UW-Stout/Heat Shock FA21
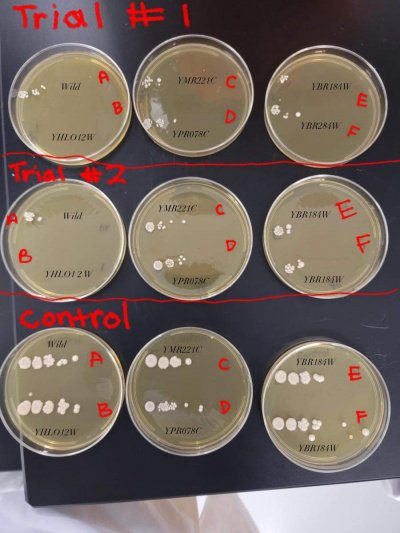
YBR284W (F)
- This yeast strain had strong growth in the control group but was very stressed by the heat shock and showed less clusters/colonies on the heat shocked trial plates. The heat shocked trial plates showed a growth decrease by 4 times.
Nitrogen Starvation
- For the YBR284W gene, results showed that there was a slight increase in growth on the dish that did not contain NH₄ where there were more colonies of yeast.
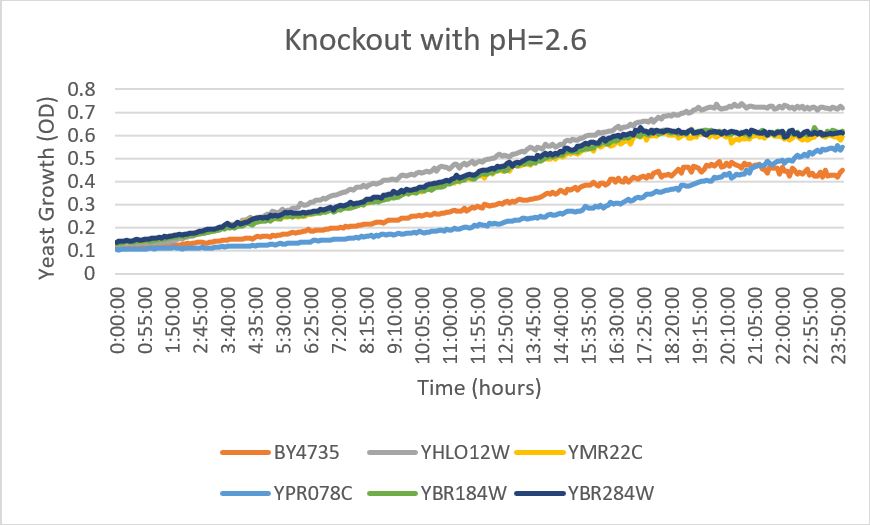
pH
YBR284W
- When this strain was exposed to a citric acid buffer with a pH of 2.6, there did not appear to be a significant change in the growth rate of the strain
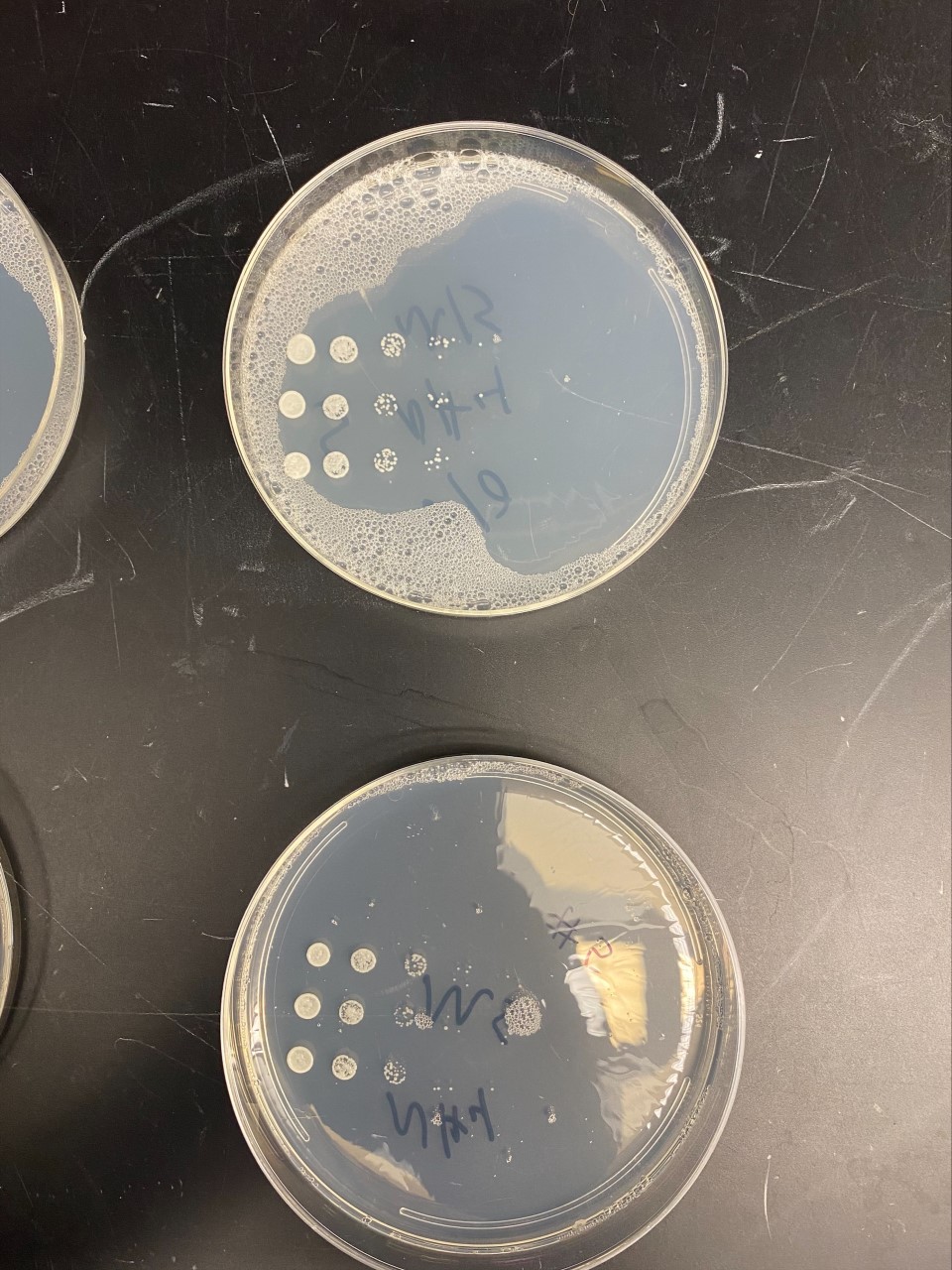
UW-Stout/Bud Scars FA21
Cells grown with this gene (YBR284W) knocked out had an average of 1.18 bud scars per cell while the wild type (BY-RY4735) had 0.85 bud scars per cell. Of 114 YBR284W cells counted, 135 bud scars were seen. This indicated that the YBR284W gene slows reproduction rate and thus bud scarring in yeast cells.
<protect>
References
See Help:References on how to add references
- ↑ Gatbonton T, et al. (2006) Telomere length as a quantitative trait: genome-wide survey and genetic mapping of telomere length-control genes in yeast. PLoS Genet 2(3):e35 SGD PMID 16552446
- ↑ Holmstrom K, et al. (1994) The sequence of a 32,420 bp segment located on the right arm of chromosome II from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 10 Suppl A:S47-62 SGD PMID 8091861
- ↑ Iwahashi H, et al. (2003) Piezophysiology of genome wide gene expression levels in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Extremophiles 7(4):291-8 SGD PMID 12910389
- ↑ Maxwell PH and Curcio MJ (2007) Host factors that control long terminal repeat retrotransposons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: implications for regulation of mammalian retroviruses. Eukaryot Cell 6(7):1069-80 SGD PMID 17496126
- ↑ Saint-Marc C, et al. (2009) Phenotypic consequences of purine nucleotide imbalance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 183(2):529-38, 1SI-7SI SGD PMID 19635936
- ↑ Willingham S, et al. (2003) Yeast genes that enhance the toxicity of a mutant huntingtin fragment or alpha-synuclein. Science 302(5651):1769-72 SGD PMID 14657499
- ↑ Xie MW, et al. (2005) Insights into TOR function and rapamycin response: chemical genomic profiling by using a high-density cell array method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102(20):7215-20 SGD PMID 15883373
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>