YBL081W
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry!
<protect>
| Systematic name | YBL081W |
| Gene name | |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr II:71866..72972 |
| Primary SGDID | S000000177 |
Description of YBL081W: Non-essential protein of unknown function; null mutation results in a decrease in plasma membrane electron transport[1][2]
</protect>
Contents
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
This gene is part of the UW-Stout Orphan Gene Project. Learn more here.
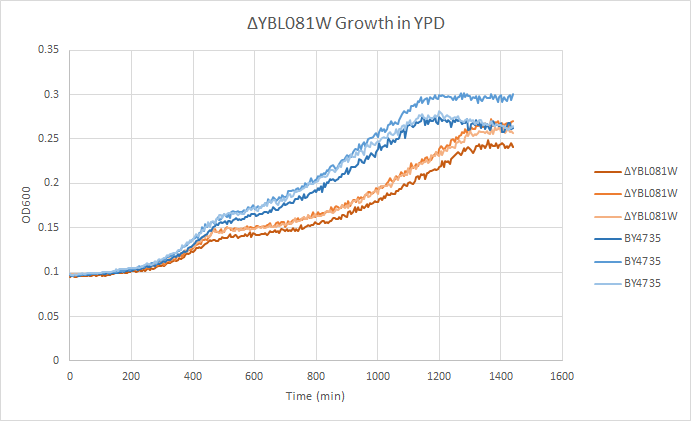
Growth in YPD
In a BY4735 background, knocking out YBL081W seems to have a moderate effect on growth rate in log-phase. In this assay, the BY4735 strain's doubling time was 414 minutes, while the YAL061 knock-out strain's doubling time was 519 minutes. (These doubling times are the means of three experiments.)
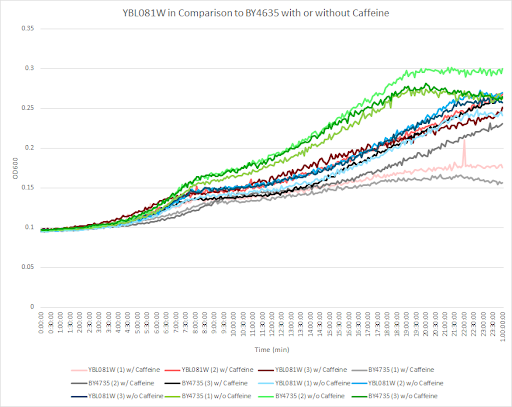
Caffeine and Yeast Cells
This graph shows the growth curve with and without caffeine. It has the knockout strain and wild type yeast cells. The caffeine enhanced the growth in both wild type and knockout strain. The average doubling time between the three experiments for the knockout strand was 741.26 minutes. The caffeine also had a positive effect on the growth curve for the wild type with the average doubling time being 1245.02 minutes. The results were concluded from the wild type and knockout strand was with this amount of caffeine it leads to an increase in growth.
The protocol can be found at
Caffeine
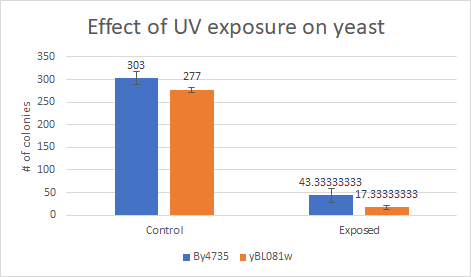
This bar graph show that compared to a BY4735 backgroung, Knocking out yBL081w make yeast more sensitive to UV light exposure
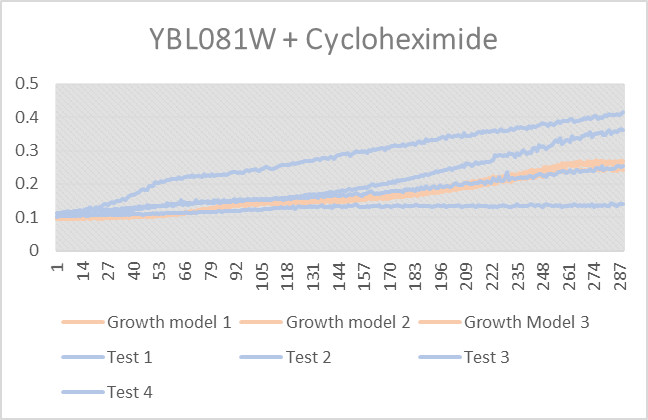
Cycloheximide on Yeast strand YBL081W
As we can tell from the figure above that Test 1 did not do well under the stress but tests 2-4 were very happy. The growth Models 1-3 are what the yeasts growth model is not stressed.
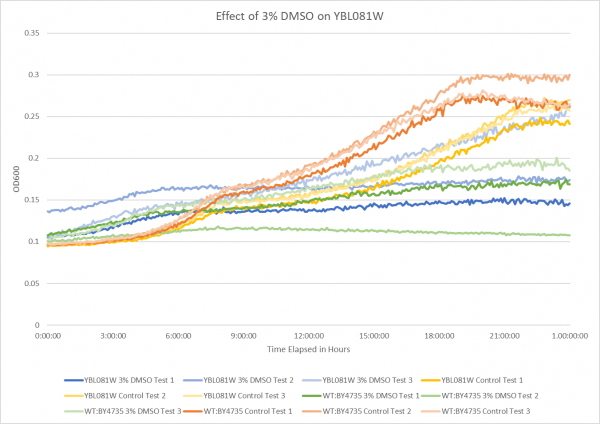
Effect of 3% DMSO on YBL081W
The graph above shows the effect of 3% DMSO on YBL081W. From the data represented the average doubling rate for the YBL081W knockout strain without DMSO was 660 minutes. When DMSO is added the average doubling time increased to 1373 minutes. This shows that 3% DMSO did add stress to this knockout strain. The average doubling time of WT:BY4735 without DMSO was 514 minutes. The average doubling rate for WT:BY4735 with DMSO was 1529 minutes. If we compare the average doubling rate of WT:BY4735 with DMSO to YBL081W with DMSO we can see that without the YBL081W gene the yeast was able to grow more quickly under DMSO induced stress.
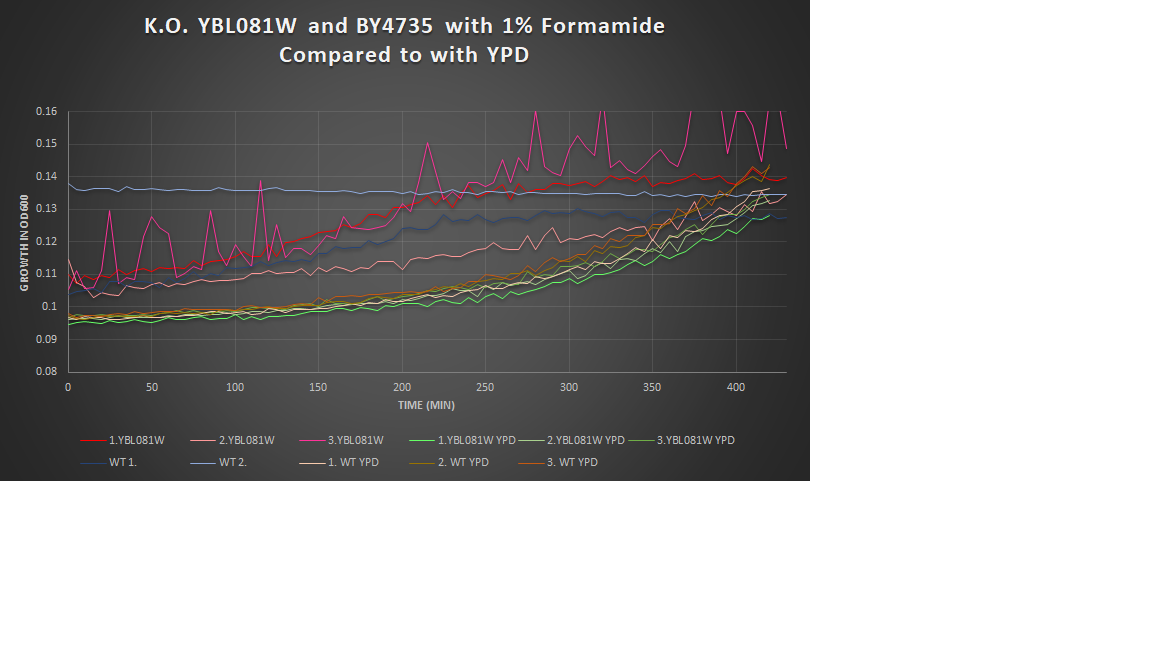
1% Formamide Yeast Torture[[1]]
This graph shows the growth curve of the knockout yeast strain YBL081W and wild type BY4735 in 1% formamide in 3 trials. The average calculated doubling time for YBL081W with 1% formamide was 2,003.40 minutes, while the unstressed strain was 3,230.61 minutes. This concluded that the stressed out strain is not sensitive to 1% formamide, and grows at a faster pace in this environment. Our stressed wild types doubling time was 2,799.18 minutes, and the unstressed was 1,823.83 minutes. Proving that the addition of 1% formamide makes this strain more sensitive to it's surroundings and leads to slower growth.
Growth in Proline and Ammonium Sulfate
This strand of yeast grew the fastest in ammonium sulfate media at 36.57 minutes as the average doubling rate. The average doubling rate in proline was 40.67 minutes, a whole 4.1 minutes slower than the average doubling rate in ammonium sulfate. The wild type also grew faster in ammonium sulfate with an average doubling rate of 46.1 minutes. In proline the average doubling rate of the wild type was 49 minutes.
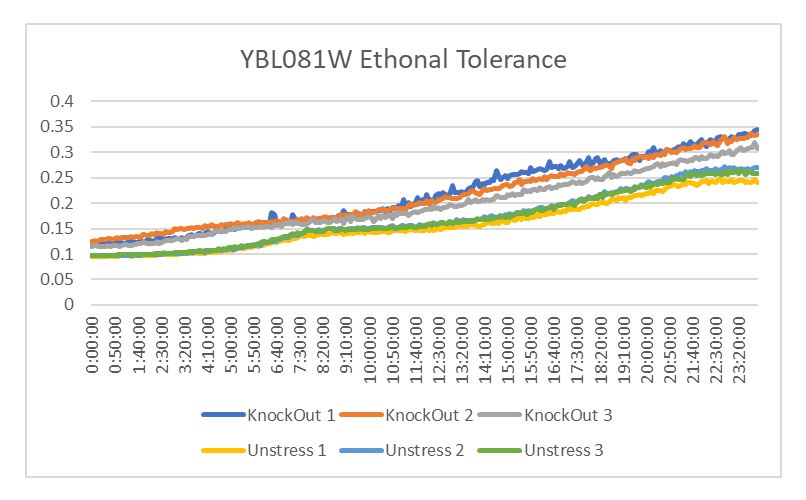
Ethanol Tolerance in YBL081W
This graph shows the growth of YBL081 treated and untreated with Ethanol. The strands of YBL081 that were treated with ethanol had a decrease in growth compared to those that weren't. The doubling time of YBL081 that was treated with ethanol is 1204.95 minutes and the doubling time of the strands that weren't is 1542.025 minutes. This shows that Ethanol leads to a decrease in growth in YBL081W.
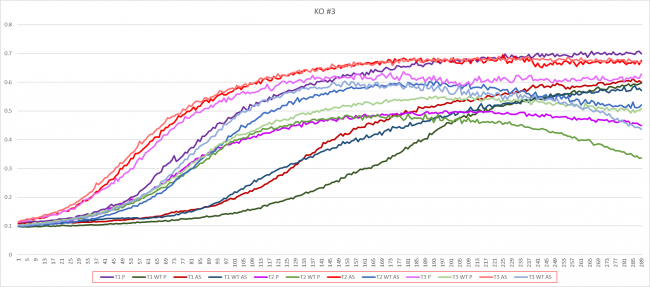
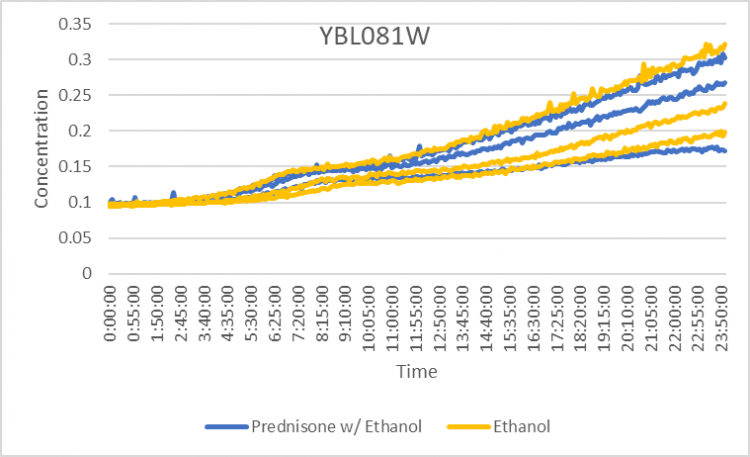
Prednisone Effects on YBL081W
The graph above shows how dilutions P2 (30 µg/ml) and E2 (10% ethanol solution) impacted the growth rate of the knockout yeast strain YBL081W over 24 hours. The concentration did not double for test 3 of P2 for this experiment so by taking only the first two test results, the doubling rate averages to around 1,120 minutes for only ethanol. As for the Prednisone with ethanol, the doubling rate averages to around 938 minutes. Overall, the Prednisone increased the rate of growth by almost 182 minutes. These results conclude that Prednisone promotes the growth of yeast cells without the YBL081W gene.
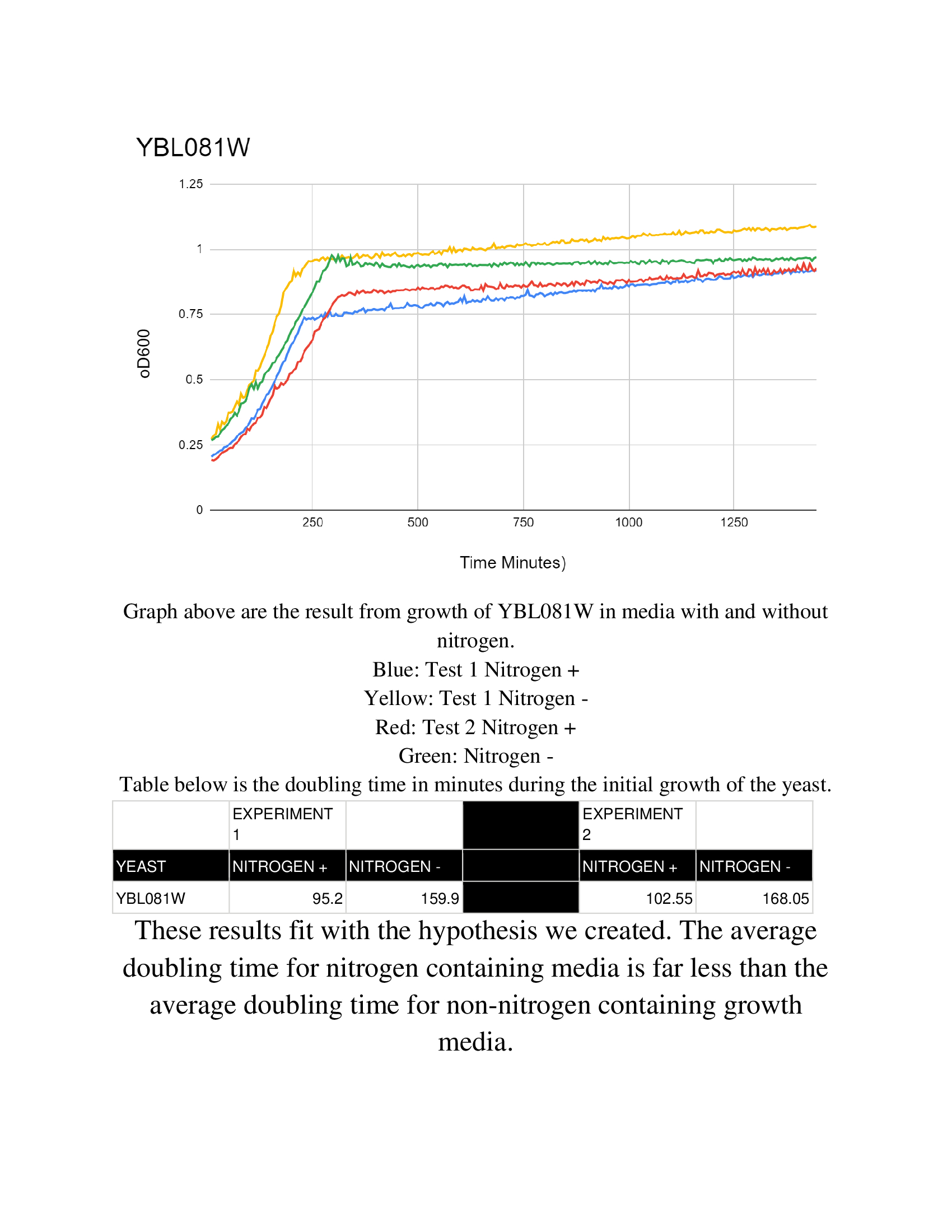
The Wild Type BY4735 has data located at the Nitrogen Starvation Protocol.
Nitrogen starvation
Hydroxyurea
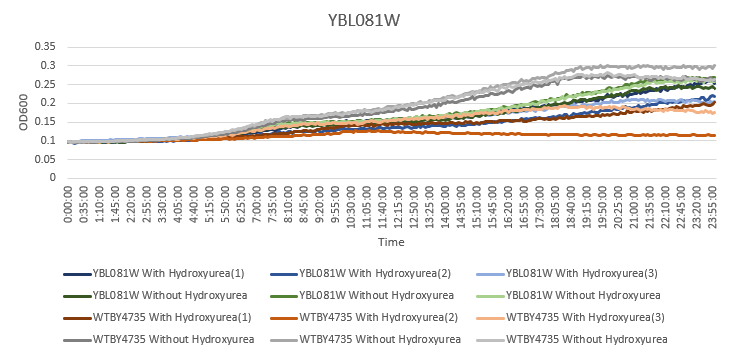 The averaging doubling time for YBL081W is 541.02 minutes. The averaging doubling time for the unstressed YBL081W is 433.29 minutes
The averaging doubling time for YBL081W is 541.02 minutes. The averaging doubling time for the unstressed YBL081W is 433.29 minutes
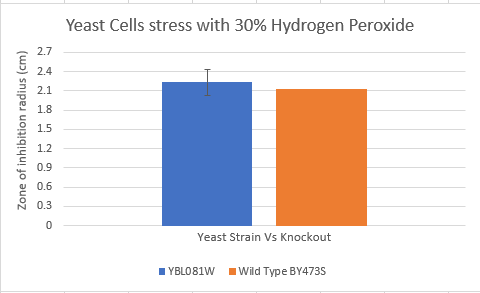
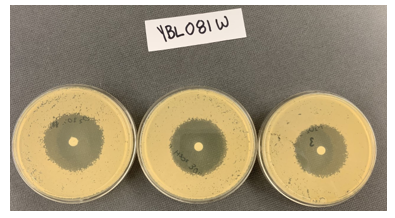
Zone of Inhibition of 30% Hydrogen Peroxide on YBL081W
References
See Help:References on how to add references
- ↑ Giaever G, et al. (2002) Functional profiling of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome. Nature 418(6896):387-91 SGD PMID 12140549
- ↑ Herst PM, et al. (2008) Plasma membrane electron transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae depends on the presence of mitochondrial respiratory subunits. FEMS Yeast Res 8(6):897-905 SGD PMID 18657191
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>