Difference between revisions of "YMR144W"
(→Bases) |
(→Bases) |
||
| Line 112: | Line 112: | ||
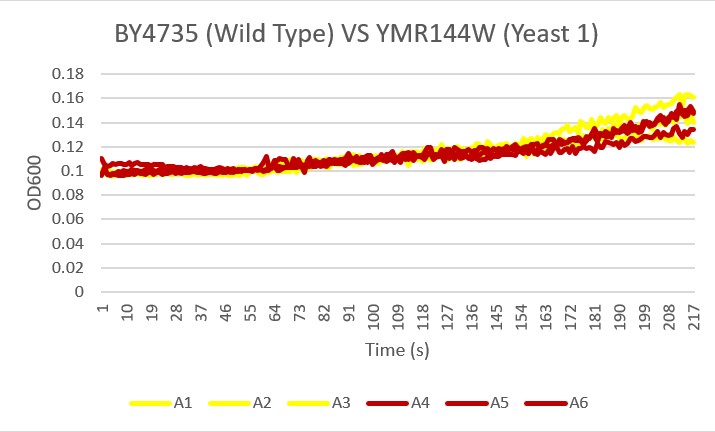
[[Image:EMwildtypeyeast1.jpg]] | [[Image:EMwildtypeyeast1.jpg]] | ||
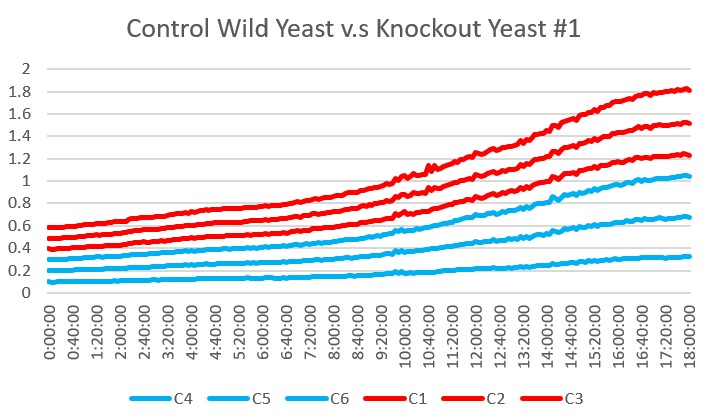
| − | '''Analysis''' Yeast 1, A4 A5 A6, showed the most similar growth trend in the basic environment compared to the wild type yeast, A1 A2 A3 over the 24 hour reading period. | + | '''Analysis''' Yeast 1, A4 A5 A6, showed the most similar growth trend in the basic environment compared to the wild type yeast, A1 A2 A3 over the 24 hour reading period. |
Protocol- | Protocol- | ||
Revision as of 13:10, 2 May 2023
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry! <protect>
| Systematic name | YMR144W |
| Gene name | |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr XIII:553362..554390 |
| Primary SGDID | S000004752 |
Description of YMR144W: Putative protein of unknown function; localized to the nucleus; YMR144W is not an essential gene[1][2]
</protect>
Contents
Acids
Analysis
These are the results we gathered from testing a pH of # against the control wild yeast and the gene YMR144W.
Isopropanol
Analysis
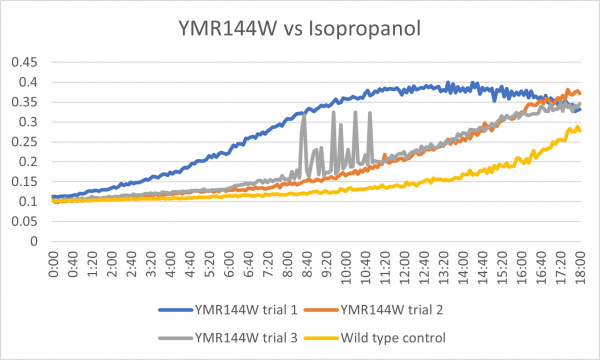
These results were not consistent as there are 3 very different results. The first trial was way off what it was supposed to be and therefore could have been contaminated or been an error in the pipetting process. The second trial was the most successful and gave the results that were expected. The third trial was good except for the region from about 8:00-11:20 where it spiked up and down. The last 2 had more growth than the control which could mean that the cell without the gene that was knocked out is able to withstand more alcohol.
Glucose Sensitivity
Protocol
Analysis
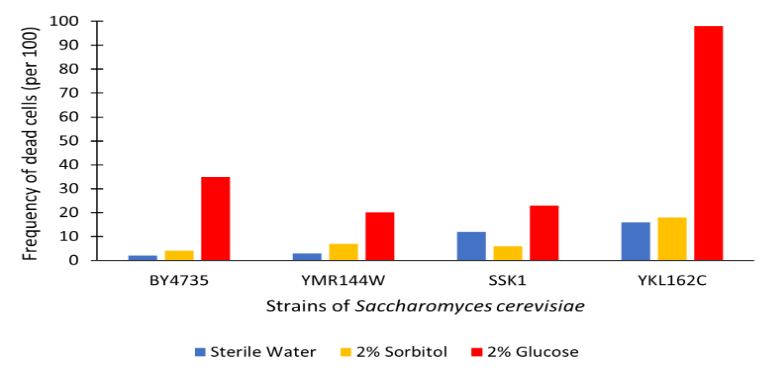
The graph displayed above shows a viability assay comparison with YMR144W knockout strain to BY4735 (wild type) and others. Results are shown as amount of dead cells per 100 assayed via hemocytometer. We found from our data that there was approximately a 15% decrease in the cell population. It was surprising to find that by removing this gene there was an increase in cell viability regarding glucose-induced apoptosis in the wild type population. Further research may be required to determine whether this resistance or lack of glucose sensitivity is linked to YMR144W for more conclusive results.
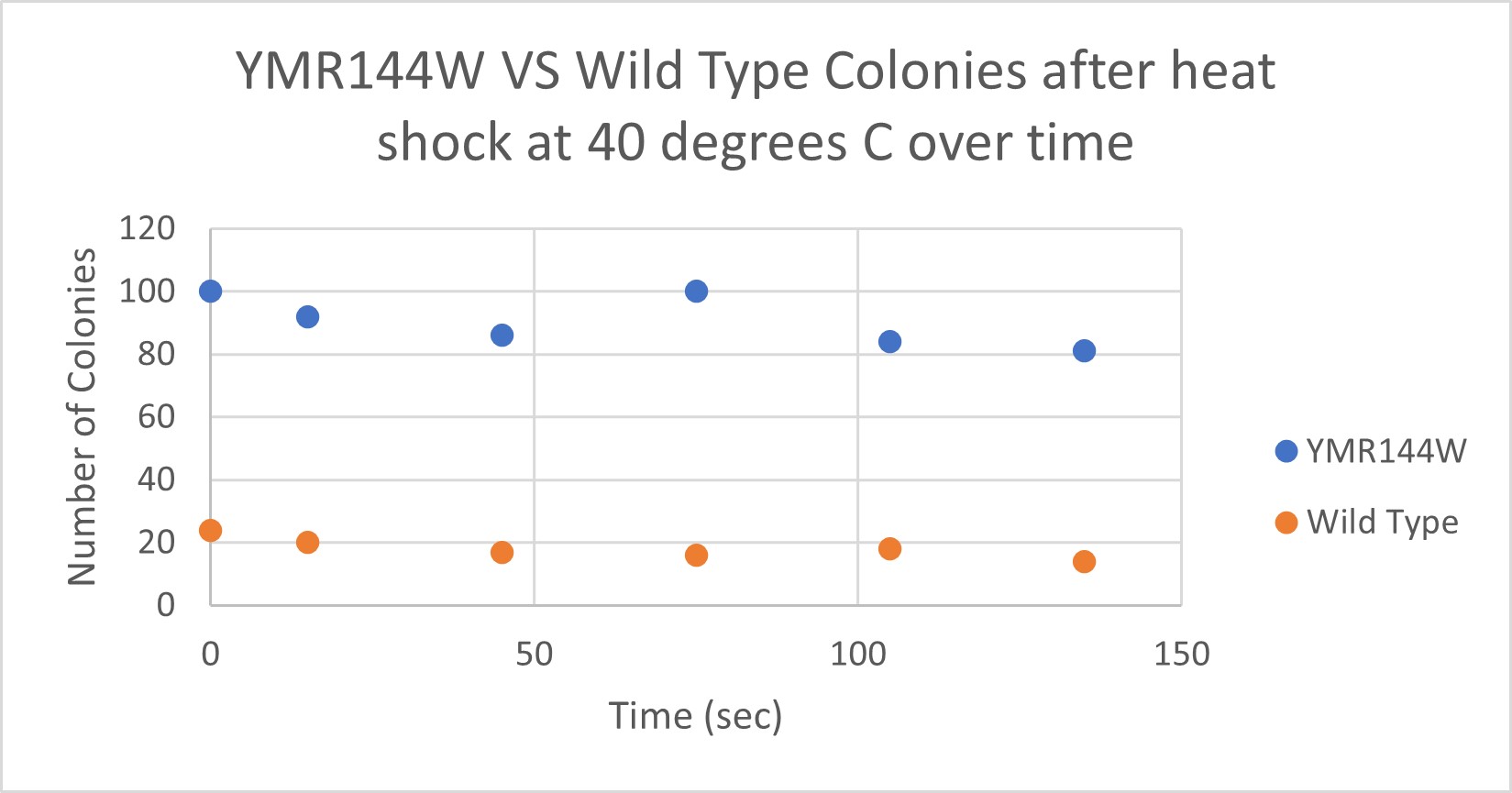
Heat Shock
| Time (sec) | Colonies | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | >100 | |
| 15 | 92 | |
| 45 | 86 | |
| 75 | 100 | |
| 105 | 84 | |
| 135 | 81 |
| Time (sec) | Colonies | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24 | |
| 15 | 20 | |
| 45 | 17 | |
| 75 | 16 | |
| 105 | 18 | |
| 135 | 14 |
Analysis
The general trend of our data yielded a negative relationship between time of heat shock. It can be inferred that with a longer amount of time we the yeast cells could continue being killed off until all of them died. Only a few of the YMR144W yeast cells died off in a matter of 135 seconds at 40 degrees Celsius. The Wild Type yeast cells were dying off at a faster rate over time compared to the YMR144W strain. This means that the gene that was knocked out in the YMR144W yeast is more senstitive to heat shock, because without that gene it is more resistant to the heat shock.
Bases
Analysis Yeast 1, A4 A5 A6, showed the most similar growth trend in the basic environment compared to the wild type yeast, A1 A2 A3 over the 24 hour reading period.
Protocol- UW-Stout/Bases SP23
References
See Help:References on how to add references
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>