Difference between revisions of "UW-Stout/Hydroxychloroquine SP21"
(→Equipment) |
(→Protocol) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
* [https://www.corning.com/worldwide/en/products/life-sciences/keymatch/3370.html Corning COSTAR 96-well clear flat-bottom assay plate] | * [https://www.corning.com/worldwide/en/products/life-sciences/keymatch/3370.html Corning COSTAR 96-well clear flat-bottom assay plate] | ||
* Wild-type yeast in 2x synthetic complete media at an OD600 of 0.1-0.2 | * Wild-type yeast in 2x synthetic complete media at an OD600 of 0.1-0.2 | ||
| − | * Hydroxychloroquine, 300 ug/uL solution in sterile water | + | * Hydroxychloroquine, 300 ug/uL solution in sterile water (as determined by the calibration protocol) |
* P20, P200 micropipettors | * P20, P200 micropipettors | ||
==Equipment== | ==Equipment== | ||
* [https://www.moleculardevices.com/sites/default/files/en/assets/data-sheets/br/spectramax-plus-384-microplate-reader.pdf Molecular Devices SpectraMax Plus 384 Microplate Reader] | * [https://www.moleculardevices.com/sites/default/files/en/assets/data-sheets/br/spectramax-plus-384-microplate-reader.pdf Molecular Devices SpectraMax Plus 384 Microplate Reader] | ||
| + | ==Precautions== | ||
| + | Use gloves and safety glasses for this experiment. Hydroxychloroquine is a potent chemical used to treat malaria and some autoimmune conditions. However, side effects include but are not limited to nausea, headache, dizziness, rash. | ||
| + | ==Calibration Protocol== | ||
| + | #Vortex the yeast culture briefly to resuspend the yeast cells. | ||
| + | #Prepare a stock solution of hydroxychloroquine 3000 ug/mL. | ||
| + | #Set up 8 wells as follows: | ||
| + | #*Well 1: 3.3uL HCQ, 46.7uL sterile water (final concentration 100ug/mL) | ||
| + | #*Well 2: 10uL HCQ, 40uL sterile water (final concentration 300ug/mL) | ||
| + | #*Well 3: 16.7uL HCQ, 33.3uL sterile water (final concentration 500ug/mL) | ||
| + | #*Well 4: 23.3uL HCQ, 26.7uL sterile water (final concentration 700ug/mL) | ||
| + | #*Well 5: 30uL HCQ, 20uL sterile water (final concentration 900ug/mL) | ||
| + | #*Well 6: 36.7uL HCQ, 13.3uL sterile water (final concentration 1100ug/mL) | ||
| + | #*Well 7: 43.3uL HCQ, 6.7uL sterile water (final concentration 1300ug/mL) | ||
| + | #*Well 8: 50uL HCQ (final concentration 1500ug/mL) | ||
| + | #Add 50uL of yeast culture to each well. | ||
| + | #Aliquot 50 uL of each stock and add 50 uL of yeast culture to each sample. | ||
| + | #To measure cell growth over a period of 24 hours, set up the plate reader as follows: | ||
| + | #*Temperature: 30°C | ||
| + | #*Mode: Kinetic | ||
| + | #*Wavelength: 600 nm | ||
| + | #*Interval: 5 minutes | ||
| + | #*Total run time: 24 hours | ||
| + | #*Shake before reading: 30 seconds. | ||
| + | #Transfer the assay plate to the reader and read for 24 hours. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Raw Data from the Calibration Protocol== | ||
| + | [[Image:Calibration.png]] | ||
| + | |||
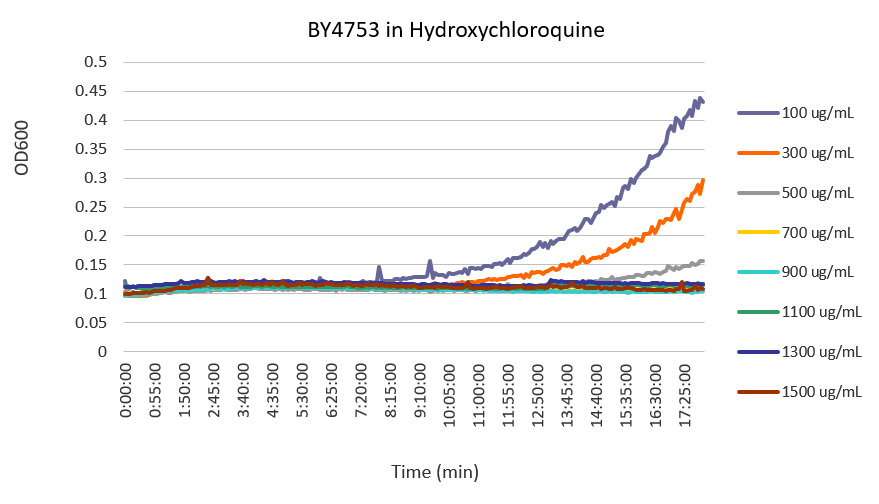
| + | Concentrations in the legend are final concentrations of hydroxychloroquine. | ||
| + | From this set of curves, a concentration of 300 ug/mL is the optimal concentration of the stressor to test the effect of hydroxychloroquine on yeast cells because it exerts enough stress over the yeast to measurably inhibit its growth, but does not prevent it from growing altogether. | ||
==Protocol== | ==Protocol== | ||
| − | + | Use the data from the calibration protocol for the optimal concentration of hydroxychloroquine. | |
| − | + | # Vortex the yeast culture briefly to resuspend the yeast cells. | |
| − | + | # Set up seven wells aliquoting 50uL of the stock hydroxychloroquine and 50uL of yeast culture. Use the seventh well for the wild-type yeast strain. | |
| − | + | #*The final concentration of hydroxychloroquine is 300ug/mL. | |
| − | + | #To measure cell growth over a period of 24 hours, set up the plate reader as follows: | |
| − | + | #*Temperature: 30°C | |
| − | + | #*Mode: Kinetic | |
| − | Temperature: 30°C | + | #*Wavelength: 600 nm |
| − | Mode: Kinetic | + | #*Interval: 5 minutes |
| − | Wavelength: 600 nm | + | #*Total run time: 24 hours |
| − | Interval: 5 minutes | + | #*Shake before reading: 30 seconds |
| − | Total run time: 24 hours | + | #Transfer the assay plate to the reader and read for 24 hours. |
| − | Shake before reading: 30 seconds | + | #*Note: Repeat the experiment a few times to account for natural variation. |
| − | |||
| − | Note: Repeat the experiment a few times to account for natural variation. | ||
Latest revision as of 07:34, 28 April 2021
Contents
Materials
- Corning COSTAR 96-well clear flat-bottom assay plate
- Wild-type yeast in 2x synthetic complete media at an OD600 of 0.1-0.2
- Hydroxychloroquine, 300 ug/uL solution in sterile water (as determined by the calibration protocol)
- P20, P200 micropipettors
Equipment
Precautions
Use gloves and safety glasses for this experiment. Hydroxychloroquine is a potent chemical used to treat malaria and some autoimmune conditions. However, side effects include but are not limited to nausea, headache, dizziness, rash.
Calibration Protocol
- Vortex the yeast culture briefly to resuspend the yeast cells.
- Prepare a stock solution of hydroxychloroquine 3000 ug/mL.
- Set up 8 wells as follows:
- Well 1: 3.3uL HCQ, 46.7uL sterile water (final concentration 100ug/mL)
- Well 2: 10uL HCQ, 40uL sterile water (final concentration 300ug/mL)
- Well 3: 16.7uL HCQ, 33.3uL sterile water (final concentration 500ug/mL)
- Well 4: 23.3uL HCQ, 26.7uL sterile water (final concentration 700ug/mL)
- Well 5: 30uL HCQ, 20uL sterile water (final concentration 900ug/mL)
- Well 6: 36.7uL HCQ, 13.3uL sterile water (final concentration 1100ug/mL)
- Well 7: 43.3uL HCQ, 6.7uL sterile water (final concentration 1300ug/mL)
- Well 8: 50uL HCQ (final concentration 1500ug/mL)
- Add 50uL of yeast culture to each well.
- Aliquot 50 uL of each stock and add 50 uL of yeast culture to each sample.
- To measure cell growth over a period of 24 hours, set up the plate reader as follows:
- Temperature: 30°C
- Mode: Kinetic
- Wavelength: 600 nm
- Interval: 5 minutes
- Total run time: 24 hours
- Shake before reading: 30 seconds.
- Transfer the assay plate to the reader and read for 24 hours.
Raw Data from the Calibration Protocol
Concentrations in the legend are final concentrations of hydroxychloroquine. From this set of curves, a concentration of 300 ug/mL is the optimal concentration of the stressor to test the effect of hydroxychloroquine on yeast cells because it exerts enough stress over the yeast to measurably inhibit its growth, but does not prevent it from growing altogether.
Protocol
Use the data from the calibration protocol for the optimal concentration of hydroxychloroquine.
- Vortex the yeast culture briefly to resuspend the yeast cells.
- Set up seven wells aliquoting 50uL of the stock hydroxychloroquine and 50uL of yeast culture. Use the seventh well for the wild-type yeast strain.
- The final concentration of hydroxychloroquine is 300ug/mL.
- To measure cell growth over a period of 24 hours, set up the plate reader as follows:
- Temperature: 30°C
- Mode: Kinetic
- Wavelength: 600 nm
- Interval: 5 minutes
- Total run time: 24 hours
- Shake before reading: 30 seconds
- Transfer the assay plate to the reader and read for 24 hours.
- Note: Repeat the experiment a few times to account for natural variation.