Difference between revisions of "YKL162C"
(→Acids) |
(→Acids) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
===Analysis=== | ===Analysis=== | ||
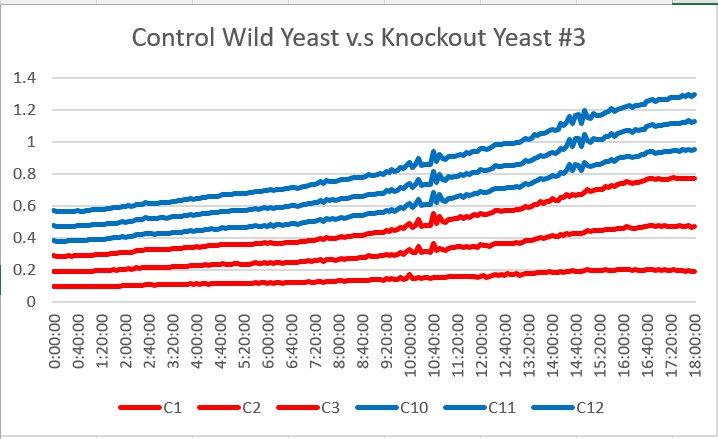
| + | These are the results we gathered from testing a pH of # against the control wild yeast and the gene YKL162C. The three red lines are the growth rates of the BY (wild yeast) mixed with a pH of # and the three blue lines are the three growth rates of the YKL162C knockout gene mixed with a pH of #. | ||
==Caffeine== | ==Caffeine== | ||
Revision as of 18:48, 2 May 2023
Share your knowledge...Edit this entry! <protect>
| Systematic name | YKL162C |
| Gene name | |
| Aliases | |
| Feature type | ORF, Uncharacterized |
| Coordinates | Chr XI:148838..147630 |
| Primary SGDID | S000001645 |
Description of YKL162C: Putative protein of unknown function; green fluorescent protein (GFP)-fusion protein localizes to the mitochondrion[1]
</protect>
Contents
Community Commentary
About Community Commentary. Please share your knowledge!
Acids
Analysis
These are the results we gathered from testing a pH of # against the control wild yeast and the gene YKL162C. The three red lines are the growth rates of the BY (wild yeast) mixed with a pH of # and the three blue lines are the three growth rates of the YKL162C knockout gene mixed with a pH of #.
Caffeine
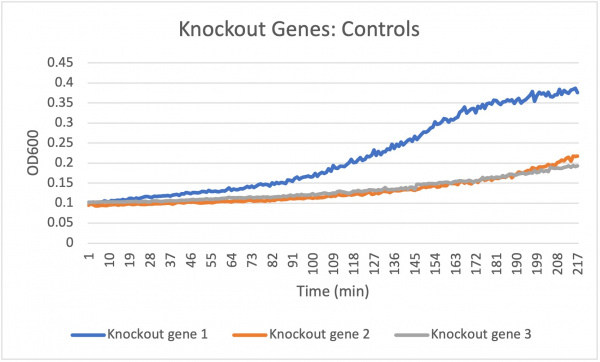
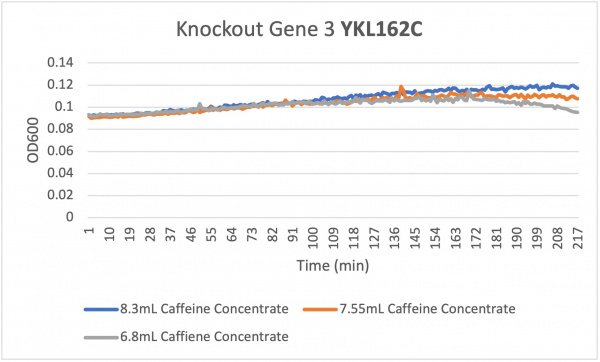
Analysis
Glucose Sensitivity
Protocol
Analysis
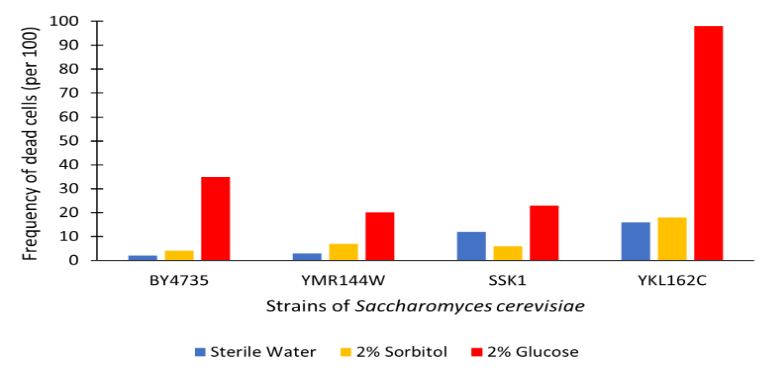
The graph displayed above shows the results of a viability assay of a YKL162C knockout strain as compared to BY4735 (wild type) and other knockout strains. This knockout strain was found to have overall more cell death than all other strains assayed. With the YKL162C gene removed nearly all cells died when incubated for 48 hours in 2% Glucose. This indicates a higher sensitivity to glucose than was exemplified in the wild type strain. There appears to be a significant associated death rate in glucose solution for this strain as compared to BY4735. Perhaps, YKL162C is of more biological importance in the BY4735 wild type than previously thought. Further research should consider why this knockout strain had complete glucose-induced apoptosis, as well as higher overall cell death rate, as compared to the other strains tested in this study.
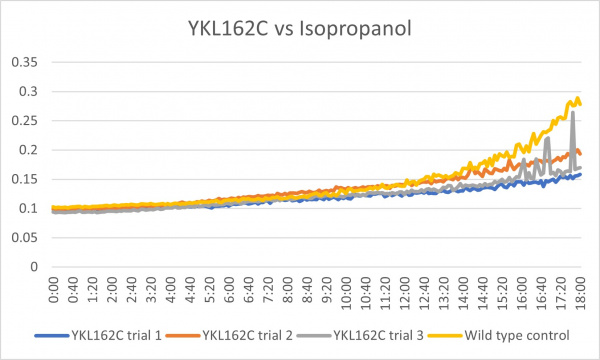
Isopropanol
Analysis
These results were what was expected and all 3 were consistent throughout the trials. Although there was less growth than the control group, it could mean that the cell is more sensitive to the isopropanol with the gene knocked out. In the third trial there was a little bit of spiking towards the end around 15:20-18:00 but other than that it was a good growth curve.
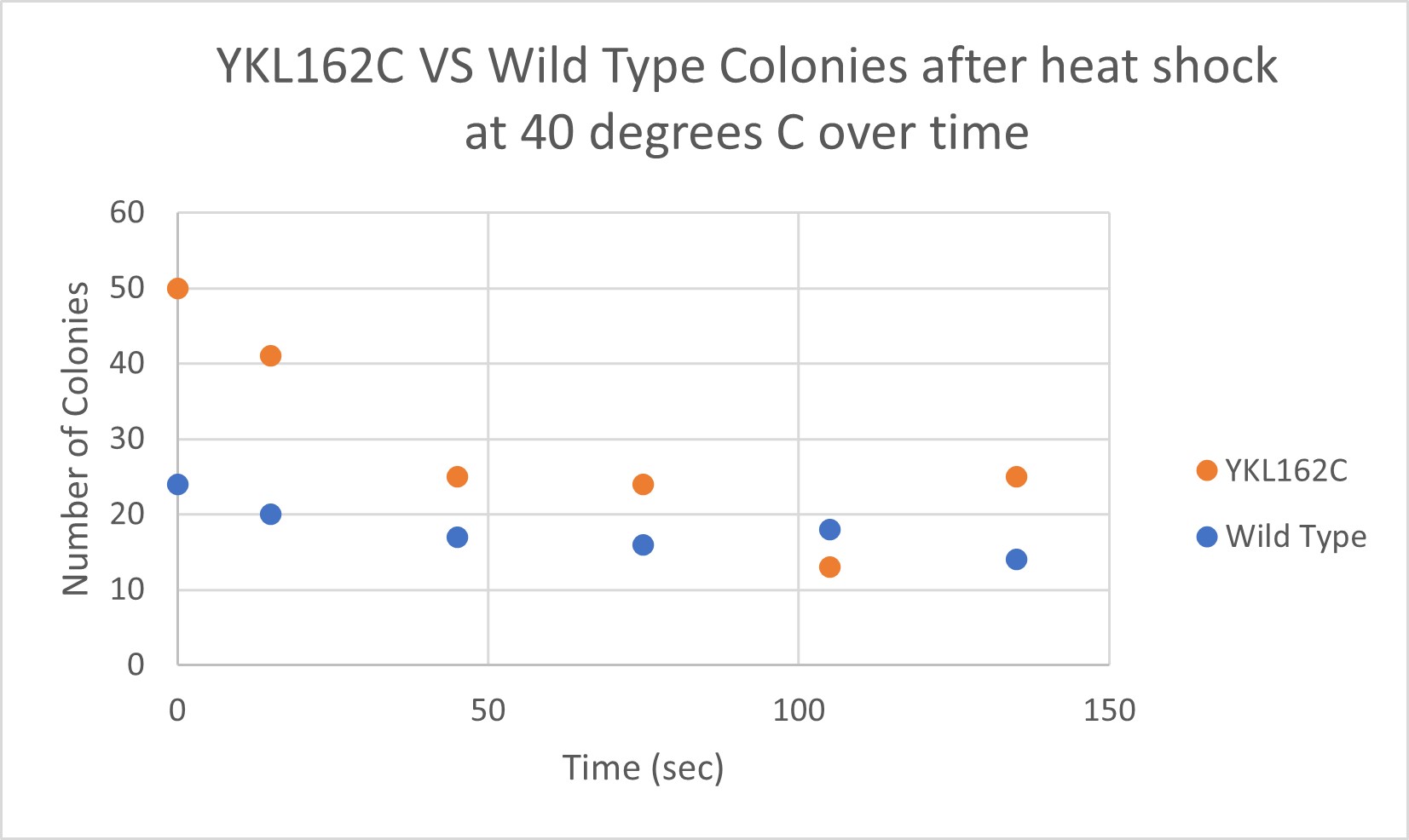
Heat Shock
| Time (sec) | Colonies | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 50 | |
| 15 | 41 | |
| 45 | 25 | |
| 75 | 24 | |
| 105 | 13 | |
| 135 | 25 |
| Time (sec) | Colonies | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24 | |
| 15 | 20 | |
| 45 | 17 | |
| 75 | 16 | |
| 105 | 18 | |
| 135 | 14 |
Analysis
The general trend of our data yielded a negative relationship between time of heat shock. About half of the yeast cells died off in a matter of 135 seconds at 40 degrees Celsius. The YKL162C yeast were dying off at a faster rate over time compared to the Wild Yeast strain. This means that the gene that was knocked out in the YKL162C yeast could have cause some resistance to heat shock.
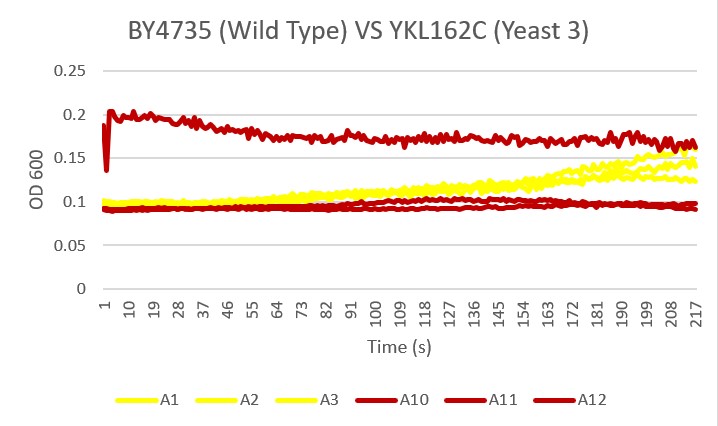
Bases
Analysis
As you can see there was clearly an error with the A11 sample of yeast 3. The other two samples showed less growth than the Wild Type yeast, A1 A2 A3, over the 24 hour time period. This knockout gene likely did not aid in basic pH environmental growth.
Protocol-
UW-Stout/Bases SP23
References
See Help:References on how to add references
See Help:Categories on how to add the wiki page for this gene to a Category </protect>