Difference between revisions of "UW-Stout/Ethanol FA22"
(→Analysis) |
(→Procedure) |
||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
#Vortex yeast culture for about 5 seconds before adding to the wells | #Vortex yeast culture for about 5 seconds before adding to the wells | ||
#Add 50 µl of wild yeast culture and 50 ul of ethanol solution into well 1 | #Add 50 µl of wild yeast culture and 50 ul of ethanol solution into well 1 | ||
| − | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 | + | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µlof ethanol solution #1 into well 2 |
| − | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 | + | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µlof ethanol solution #2 into well 3 |
| − | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 | + | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µl of ethanol solution #3 into well 4 |
| − | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 | + | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µl of ethanol solution #4 into well 5 |
| − | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 | + | #Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µl of ethanol solution #5 into well 6 |
#Put your well clear flat-bottom assay plate into the incubator and let sit | #Put your well clear flat-bottom assay plate into the incubator and let sit | ||
#Wait and observe the growth | #Wait and observe the growth | ||
Revision as of 13:16, 13 December 2022
Contents
Yeast Ethanol Stress Experiment
Introduction
We will add a sample of ethanol solution to a yeast culture and measure the growth afterward. This experiment is to determine what amounts of ethanol solution are best for the stress experiment on our class knockout genes.
Materials
- Corning COSTAR 96-well clear flat-bottom assay plate
- Wild-type yeast in 2x synthetic complete media at an OD600 of 0.1-0.2
- Ethanol concertation of 1M (labeled ETH01M)
- Sterile water
Procedure
- Turn on the biological safety cabinet
- Steralize your hands and other materials you need in the biological safety cabinet
- Complete steps 4-20 in the biological safety cabinet
- Make the ethanol solution in a 1.7 ml PCR tube by adding 942µl of water and 58µl of 100% ethanol
- Collect well a clear flat-bottom assay plate
- Vortex yeast culture for about 5 seconds
- Put 50µl of the yeast culture into all 12 wells.
- In the 1st well add 1µl of your ethanol solution and 49µl of H2O
- In the 2nd well add 2µl of your ethanol solution and 48µl of H2O
- In the 3rd well add 3µl of your ethanol solution and 47µl of H2O
- In the 4th well add 4µl of your ethanol solution and 46µl of H2O
- In the 5th well add 5µl of your ethanol solution and 45µl of H2O
- In the 6th well add 8µl of your ethanol solution and 42µl of H2O
- In the 7th well add 10µl of your ethanol solution and 40µl of H2O
- In the 8th well add 20µl of your ethanol solution and 30µl of H2O
- In the 9th well add 27µl of your ethanol solution and 23µl of H2O
- In the 10th well add 35µl of your ethanol solution and 15µl of H2O
- In the 11th well add 41µl of your ethanol solution and 9µl of H2O
- In the 12th well add 50µl of your ethanol solution and 0µl of H2O
- In E column 12th well add 0µl of your ethanol solution and 50µl of H2O
- Put your well clear flat-bottom assay plate into the incubator and let sit.
- Wait and observe the growth or death
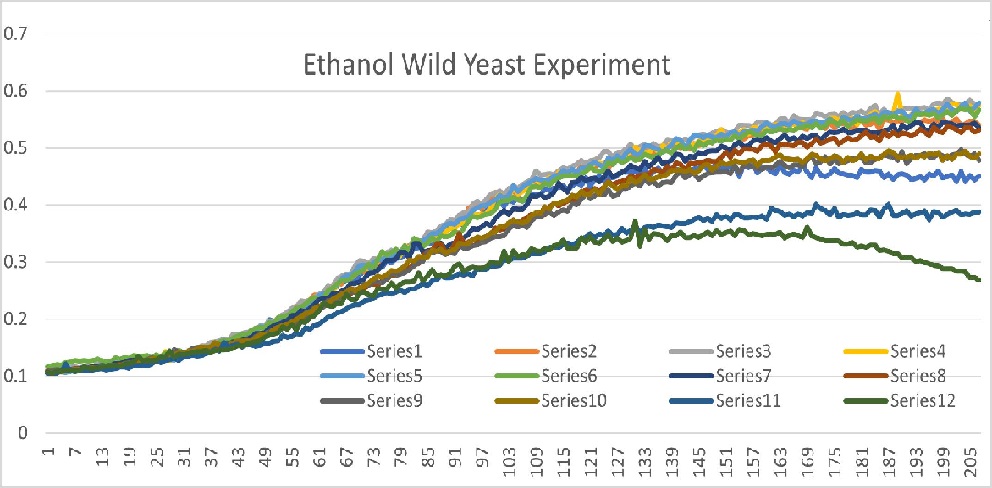
Data
Analysis
Well 1 through 10 had roughly the same growth curve with linear movement from 25 minutes to 103 minutes. It plateaus starting at 103 minutes. Well 11 had a slow growth and the curve plateaued out just under 0.4 OD600. Well 12 also had a slow growth and the curve is concave down parabola shape that peaks at 0.37 OD600. Well 11 and 12 were our outliers because it did not fit into our expected curve.
Knockout Yeast Ethanol Stress Experiment
Introduction
Our class had some success with knocking out certain yeast genes. We take these genes, add the ethanol solution to a culture of said knockout genes and see how the yeast without those genes live or not.
Materials
- Corning COSTAR 96-well clear flat-bottom assay plate
- Wild-type yeast in 2x synthetic complete media at an OD600 of 0.1-0.2
- Ethanol concertation of 1M (labeled ETH01M)
- Sterile water
*BY-BY4735 (wild type)
- YJL133C-A yeast knockout strand
- YER186C yeast knockout strand
- YER076C yeast knockout strand
- YHR033W yeast knockout strand
- YCR095C yeast knockout strand
Procedure
- Turn on biological safety cabinet
- Steralize your hands and any other materials you need in the biological safety cabinet
- Complete steps 4-13 in the biological safety cabinet
- Make/find your ethanol solution, add 942µl of water and 58µl of neat ethanol in a 1.7ml PCR tube
- Collect well a clear flat-bottom assay plate
- Vortex yeast culture for about 5 seconds before adding to the wells
- Add 50 µl of wild yeast culture and 50 ul of ethanol solution into well 1
- Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µlof ethanol solution #1 into well 2
- Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µlof ethanol solution #2 into well 3
- Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µl of ethanol solution #3 into well 4
- Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µl of ethanol solution #4 into well 5
- Add 50 µl of knockout strain yeast culture and 50 µl of ethanol solution #5 into well 6
- Put your well clear flat-bottom assay plate into the incubator and let sit
- Wait and observe the growth
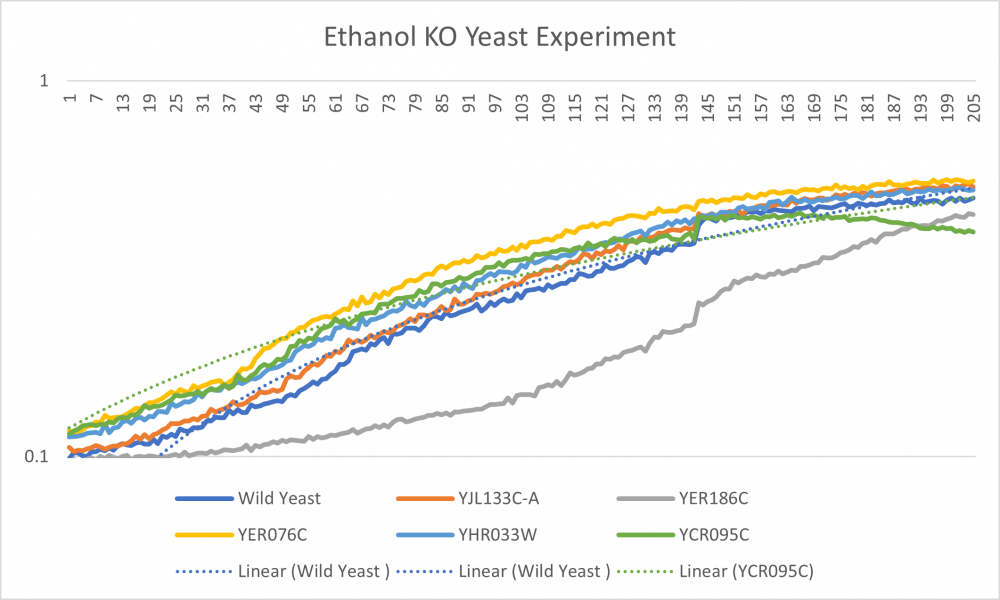
Data
Analysis
-Well 1 with the wild type had a steady growth throughout the experiment. Doubling time is 71.76
-Well 2 line lies on the middle of the overall growth curve. Doubling time is 67.78
-Well 3 is the outlier. The Ethanol dramatically decreased cell growth. The doubling time is 189.60
-Well 4 had the largest cell growth. Doubling time is 71.60
-Well 5 is slightly above well 2 but has a similar curve. Doubling time is 76.63
-Well 6 cell growth started off at a higher growth rate but decreased at an earlier rate. The doubling time is 60.40
-Overall we observed the growth of yeast cells when introduced to Ethanol. With our Ethanol concentration, the yeast cells became stressed out while still having cell growth.