Difference between revisions of "SGD Newsletter, December 2023"
(→Textpresso updated) |
(→SGD's Social Media Footprint is Expanding) |
||
| (49 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category: Newsletter]] | [[Category: Newsletter]] | ||
| − | '''About this newsletter:''' <br> This is the December 2023 issue of the SGD newsletter. The goal of this newsletter is to inform our users about new features in SGD and to foster communication within the yeast community. You can view this [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/SGD_Newsletter, | + | '''About this newsletter:''' <br> This is the December 2023 issue of the SGD newsletter. The goal of this newsletter is to inform our users about new features in SGD and to foster communication within the yeast community. You can view this [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/SGD_Newsletter,_December_2023 newsletter] as well as previous newsletters, on the SGD [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/SGD_Newsletter_Archives Community Wiki]. |
==Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.4== | ==Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.4== | ||
The ''S. cerevisiae'' strain S288C reference genome annotation was updated. The new genome annotation is release R64.4.1, dated 2023-08-23. Note that the underlying genome sequence itself was not altered in any way. | The ''S. cerevisiae'' strain S288C reference genome annotation was updated. The new genome annotation is release R64.4.1, dated 2023-08-23. Note that the underlying genome sequence itself was not altered in any way. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
*[https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/YPR108W-A YPR108W-A] | *[https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/YPR108W-A YPR108W-A] | ||
| − | Various sequence and annotation files are available on SGD’s Downloads site. You can find more update details on the Details of 2023 Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.4 SGD Wiki page. | + | Various sequence and annotation files are available on SGD’s [http://sgd-archive.yeastgenome.org Downloads] site. You can find more update details on the [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/Details_of_2023_Reference_Genome_Annotation_Update_R64.4 Details of 2023 Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.4] SGD Wiki page. |
| − | ==Textpresso updated== | + | ==Full-text search tool Textpresso updated== |
| − | + | [[Image:textpressoLogo.png |thumb|left|https://www.alliancegenome.org/textpresso/sgd/|upright=1.25]] | |
| − | [ | + | SGD’s instance of [https://www.alliancegenome.org/textpresso/sgd/tpc/search Textpresso] has recently been updated! Each week, SGD biocurators triage new publications from PubMed to load the newest yeast papers into the database. Once they are in SGD, those papers get indexed and loaded into Textpresso – a tool for full-text mining and searching. '''This is the new part:''' Content updates in SGD’s Textpresso are now happening on a weekly basis, meaning you can search full text of the very latest yeast papers! |
You already love Textpresso for searching full text and its other bells and whistles: | You already love Textpresso for searching full text and its other bells and whistles: | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
*Search location options can constrain to specific sections of papers | *Search location options can constrain to specific sections of papers | ||
| − | Textpresso can be accessed via the “Full-text Search” link under “Literature” in the purple toolbar that runs across the top of most SGD webpages. Now you can search full text of the very latest yeast papers each week! | + | Textpresso can be accessed via the [https://www.alliancegenome.org/textpresso/sgd/tpc/search “Full-text Search”] link under “Literature” in the purple toolbar that runs across the top of most SGD webpages. Now you can search full text of the very latest yeast papers each week! |
==Biochemical Pathways now in SGD Search== | ==Biochemical Pathways now in SGD Search== | ||
| − | [[Image:yeastPathwaysLogo.png |thumb|left|upright=1.25]] | + | [[Image:yeastPathwaysLogo.png |thumb|left|https://pathway.yeastgenome.org|upright=1.25]] |
| − | YeastPathways, which is the database of metabolic pathways and enzymes in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is manually curated and maintained by the curation team at SGD. | + | [https://pathway.yeastgenome.org YeastPathways], which is the database of metabolic pathways and enzymes in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is manually curated and maintained by the curation team at SGD. |
| − | This resource is jam-packed with information, but somewhat hidden from view. To make the pathways more readily accessible, some time ago we added a new section with pathways links on the relevant gene pages. Now the pathways are available in SGD Search! | + | This resource is jam-packed with information, but somewhat hidden from view. To make the pathways more readily accessible, some time ago we added a new section with pathways links on the relevant gene pages. Now the pathways are available in [https://www.yeastgenome.org/search?q=&category=pathway SGD Search]! |
The category “Biochemical Pathways” is now available, with facets (i.e., subcategories) for References and Loci. For even easier access, we also added the Pathway names and IDs to the autocomplete in the Search box, to enable quick browsing. Enjoy! | The category “Biochemical Pathways” is now available, with facets (i.e., subcategories) for References and Loci. For even easier access, we also added the Pathway names and IDs to the autocomplete in the Search box, to enable quick browsing. Enjoy! | ||
==microPublications - latest yeast papers== | ==microPublications - latest yeast papers== | ||
| − | [[Image:MicroPub.png|link=https://www.micropublication.org/|thumb|right|upright=.4]] | + | [[Image:MicroPub.png|link=https://www.micropublication.org/|thumb|right|https://www.micropublication.org|upright=.4]] |
| − | [https://www.micropublication.org microPublication Biology] is part of the emerging genre of rapidly-published research communications. We are seeing a strong set of microPublications come through the database and are glad for this venue to publish brief, novel findings, negative and/or reproduced results, and results which may initially lack a broader scientific narrative. Each article is peer-reviewed, assigned a DOI, and indexed through PubMed and PubMedCentral. | + | [https://www.micropublication.org microPublication Biology] is part of the emerging genre of rapidly-published research communications. We are seeing a strong set of microPublications come through the database and are glad for this venue to publish brief, novel findings, negative and/or reproduced results, and results which may initially lack a broader scientific narrative. Each article is peer-reviewed, assigned a DOI, and indexed through [https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov PubMed] and [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/ PubMedCentral]. |
Consider [https://www.micropublication.org/journals/biology/species/s-cerevisiae microPubublications] when you have a result that doesn't necessarily fit into a larger story, but will be of value to others. | Consider [https://www.micropublication.org/journals/biology/species/s-cerevisiae microPubublications] when you have a result that doesn't necessarily fit into a larger story, but will be of value to others. | ||
| − | Latest yeast microPublications: | + | Latest [https://www.micropublication.org/journals/biology/species/s-cerevisiae yeast microPublications]: |
*[https://www.yeastgenome.org/reference/S000345614 Bennett SA, Cobos SN, Son E, Segal R, Mathew S, Yousuf H, Torrente MP (2023)] Impaired RNA Binding Does Not Prevent Histone Modification Changes in a FUS ALS/FTD Yeast Model. MicroPubl Biol 2023 | *[https://www.yeastgenome.org/reference/S000345614 Bennett SA, Cobos SN, Son E, Segal R, Mathew S, Yousuf H, Torrente MP (2023)] Impaired RNA Binding Does Not Prevent Histone Modification Changes in a FUS ALS/FTD Yeast Model. MicroPubl Biol 2023 | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
All yeast microPublications can be found in [https://www.yeastgenome.org/search?category=reference&journal=microPublication.%20Biology&page=0&q= SGD]. | All yeast microPublications can be found in [https://www.yeastgenome.org/search?category=reference&journal=microPublication.%20Biology&page=0&q= SGD]. | ||
| − | ==Allele SGDIDs added to YeastMine== | + | ==Updates to SGD's YeastMine data warehouse== |
| − | YeastMine is SGD’s data warehouse, powered by InterMine. We have so many templates (i.e., pre-defined queries) that provide access to so many different kinds of data. | + | [[Image:yeastmineLogo.png |thumb|right|https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/|upright=1.25]] |
| + | ===Allele SGDIDs added to YeastMine=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/begin.do YeastMine] is SGD’s data warehouse, powered by InterMine. We have so many templates (i.e., pre-defined queries) that provide access to so many different kinds of data. | ||
A big area of focus for SGD and the yeast community is alleles. Alleles are different versions of genes that vary in DNA and sometimes protein sequence. Did you know that you can easily and quickly get all curated yeast allele data directly from YeastMine? | A big area of focus for SGD and the yeast community is alleles. Alleles are different versions of genes that vary in DNA and sometimes protein sequence. Did you know that you can easily and quickly get all curated yeast allele data directly from YeastMine? | ||
| − | + | The [https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Gene_Alleles&scope=all Genes -> Alleles] template returns data for one gene or a list of genes or the entire genome! Data include standard and systematic names for genes, gene name descriptions, allele names and descriptions, allele types, aliases, and references. SGDIDs for genes are included, and now SGDIDs for the alleles have been added. Previously, this query returned all of these data without the SGDIDs for the alleles. Based on user feedback, we have now made these allele SGDIDs available, so that they can be used to identify and distinguish different alleles. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ==Downloads files added to YeastMine== | + | ===Downloads files added to YeastMine=== |
| − | |||
| − | [ | + | Back in the day, SGD maintained an FTP site to distribute data in various files. More recently, you have found these files in the [http://sgd-archive.yeastgenome.org SGD Downloads] site. We have now moved these files to [https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/begin.do YeastMine]: |
From the YeastMine homepage, click Templates at top left. In the Filter, select ‘Downloads’ to constrain the list of templates. | From the YeastMine homepage, click Templates at top left. In the Filter, select ‘Downloads’ to constrain the list of templates. | ||
| − | The following templates are listed under Downloads: | + | The following query templates are listed under Downloads: |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Deleted_Merged_Features_Tab&scope=all Deleted Merged Features]: Retrieve all deleted and merged features. | |
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Func_Comp_Tab&scope=all Retrieve Functional Complementation] for genes: For gene(s), retrieve information about cross-species functional complementation between yeast and another species. | ||
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=GO_Terms_Tab&scope=all Retrieve GO Terms]: Retrieve GO Terms, including name, ID, namespace, and definition. | ||
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=SGD_Chr_Features_Tab&scope=all Retrieve SGD chromosomal Features]: Retrieve genes and other chromosomal features, including IDs, coordinates, and descriptions. | ||
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=CrossRefs_Tab&scope=all Retrieve all cross-references] for all genes: Retrieve IDs for yeast gene and gene products in other databases. | ||
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Domains_Tab&scope=all Retrieve all domains] of all genes: Retrieve Proteins/Genes that have a given domain. | ||
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Interaction_Tab&scope=all Retrieve all interactions] for all genes: Retrieve physical and genetic interactions for all genes. | ||
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Pathways_Tab&scope=all Retrieve all pathways] for all genes: Retrieve all metabolic pathways for all genes. | ||
| + | *[https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Protein_Properties_Tab&scope=all Retrieve protein properties] of all proteins of ORFs: Retrieve protein properties, including pI, molecular weight, N-terminal and C-terminal sequences, codon bias, etc. of all proteins. | ||
| − | + | For help using YeastMine, please see the [https://sites.google.com/view/yeastgenome-help/analyze-help/yeastmine SGD Help Pages] and our [https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PL0VHJdmmIuj-b00aNRfqwMe9TvkfWWcyZ YeastMine playlist] on the [https://www.youtube.com/SaccharomycesGenomeDatabase SGD YouTube Channel]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | For help using YeastMine, please see the SGD Help Pages and YouTube Channel. | ||
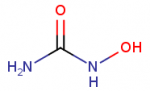
==Chemical structures now on Chemical pages in SGD== | ==Chemical structures now on Chemical pages in SGD== | ||
| − | SGD curators use the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) Ontology, maintained by EMBL-EBI, to describe chemicals used in experiments curated from yeast publications and displayed on SGD webpages. | + | [[Image:hydroxyurea2.png |thumb|right|Hydroxyurea CHEBI:44423|upright=0.5]] |
| − | + | SGD curators use the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest ([https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ ChEBI]) Ontology, maintained by [https://www.ebi.ac.uk EMBL-EBI], to describe chemicals used in experiments curated from yeast publications and displayed on SGD webpages. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | Click the structure to zoom in, click again to zoom back out. | + | You may have noticed that we have recently added chemical structures provided by ChEBI to the [https://www.yeastgenome.org/search?q=&category=chemical Chemical pages] in SGD! Click the structure to zoom in, click again to zoom back out. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
It’s a small detail, but we love this feature, and hope that you do too! Thanks, ChEBI! | It’s a small detail, but we love this feature, and hope that you do too! Thanks, ChEBI! | ||
==Alliance of Genome Resources - Release 6.0== | ==Alliance of Genome Resources - Release 6.0== | ||
| − | [[Image:alliance_logo.png| | + | [[Image:alliance_logo.png|thumb|left|https://www.alliancegenome.org|upright=.725]] |
The [https://www.alliancegenome.org/ Alliance of Genome Resources], a collaborative effort between SGD and other model organism databases (MOD), released [https://www.alliancegenome.org/release-notes version 6.0] in September 2023. | The [https://www.alliancegenome.org/ Alliance of Genome Resources], a collaborative effort between SGD and other model organism databases (MOD), released [https://www.alliancegenome.org/release-notes version 6.0] in September 2023. | ||
'''Version 6.0''' adds new features to gene pages: | '''Version 6.0''' adds new features to gene pages: | ||
| − | *New Paralogy section. Similar to Orthology, the Paralogy data are sourced from the DRSC’s [https://fgr.hms.harvard.edu/diopt DIOPT] tool, which lets you view predictions from several tools at one time. Each table is ranked based on similarity, identity, alignment length, and a count of algorithms (methods) used to predict a paralogous match. See human HSPA1A gene page for an example. | + | *New Paralogy section. Similar to Orthology, the Paralogy data are sourced from the DRSC’s [https://fgr.hms.harvard.edu/diopt DIOPT] tool, which lets you view predictions from several tools at one time. Each table is ranked based on similarity, identity, alignment length, and a count of algorithms (methods) used to predict a paralogous match. See human [https://www.alliancegenome.org/gene/HGNC:5232#paralogy HSPA1A] gene page for an example. |
*New Sequence Detail section. For different transcripts of the gene, you can choose to view the sequence for the gene, or its CDS, cDNA, protein, gene with collapsed introns, or genomic sequence with or without 500 bp up and downstream. | *New Sequence Detail section. For different transcripts of the gene, you can choose to view the sequence for the gene, or its CDS, cDNA, protein, gene with collapsed introns, or genomic sequence with or without 500 bp up and downstream. | ||
*Disease Qualifier. The qualifier describes whether a gene may be, for example, a marker_for the onset of a disease, or implicated_in the severity of a disease. | *Disease Qualifier. The qualifier describes whether a gene may be, for example, a marker_for the onset of a disease, or implicated_in the severity of a disease. | ||
| Line 149: | Line 128: | ||
*The Source column entries now link back to their respective resource webpages. | *The Source column entries now link back to their respective resource webpages. | ||
</p> | </p> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==SGD's Social Media Footprint is Expanding== | ||
| + | [[Image:newSocialMedia2.png |thumb|right|SGD is on new social media|upright=0.75]] | ||
| + | Discourse, Mastodon, BlueSky - oh my! Social media is in a chaotic period, with once tight-knit communities having been dismantled and thrown into the ether. SGD feels your pain; we have been searching for our audience, waiting for the stardust to settle, coagulate, coalesce.... In the interim, in an effort to reach you, we have set up SGD outposts on various platforms: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Discourse''': The [https://community.alliancegenome.org/c/model-organism-yeast/8 Alliance of Genome Resources Community Forum] brings together communities of the major model organisms - yeast, worm, fly, zebrafish, frog, rat, and mouse - in one place. Users can create accounts to post announcements and questions, and chat with other researchers in a science-focused arena. [mailto:sgd-helpdesk@lists.stanford.edu Contact SGD] for an invited account, which has additional permissions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://joinmastodon.org '''Mastodon''']: We're just getting started with Mastodon; follow SGD at [https://genomic.social/@yeastgenome @yeastgenome@genomic.social] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://bsky.app '''BlueSky''']: We've also just begun with BlueSky; follow SGD at [https://bsky.app/profile/yeastgenome.bsky.social @yeastgenome.bsky.social] | ||
| + | |||
| + | We will be cross-posting to the various accounts - come find SGD on these platforms and we can navigate this latest social media adventure together! | ||
==Upcoming Conferences and Courses== | ==Upcoming Conferences and Courses== | ||
| Line 174: | Line 165: | ||
**Cape Town International Convention Centre, Cape Town, South Africa | **Cape Town International Convention Centre, Cape Town, South Africa | ||
**September 29 to October 03, 2024 | **September 29 to October 03, 2024 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Happy Holidays from SGD!== | ||
| + | [[File:SnowShmoo.png|thumb|left|upright=.25]] | ||
| + | We want to take this opportunity to wish you and your family, friends and lab mates the best during the upcoming holidays. '''Stanford University will be closed for two weeks starting December 21''', reopening on January 4th, 2024. Although SGD staff members will be taking time off, the website will be up and running throughout the winter break, and we will resume responding to user requests and questions in the new year. | ||
Latest revision as of 12:13, 13 December 2023
About this newsletter:
This is the December 2023 issue of the SGD newsletter. The goal of this newsletter is to inform our users about new features in SGD and to foster communication within the yeast community. You can view this newsletter as well as previous newsletters, on the SGD Community Wiki.
Contents
- 1 Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.4
- 2 Full-text search tool Textpresso updated
- 3 Biochemical Pathways now in SGD Search
- 4 microPublications - latest yeast papers
- 5 Updates to SGD's YeastMine data warehouse
- 6 Chemical structures now on Chemical pages in SGD
- 7 Alliance of Genome Resources - Release 6.0
- 8 SGD's Social Media Footprint is Expanding
- 9 Upcoming Conferences and Courses
- 10 Happy Holidays from SGD!
Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.4
The S. cerevisiae strain S288C reference genome annotation was updated. The new genome annotation is release R64.4.1, dated 2023-08-23. Note that the underlying genome sequence itself was not altered in any way.
This annotation update included:
new uORFs for 3 ORFs:
8 new ncRNAs:
- SUT035/YNCC0015W
- SUT053/YNCD0033W
- SUT468/YNCD0034C
- SUT532/YNCG0047C
- SUT125/YNCG0048W
- SUT126/YNCG0049W
- SUT390/YNCP0025W
- SUT418/YNCP0026W
3 ORFs demoted from ‘Uncharacterized’ to ‘Dubious’ based on request from NCBI because they overlap tRNAs:
Various sequence and annotation files are available on SGD’s Downloads site. You can find more update details on the Details of 2023 Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.4 SGD Wiki page.
Full-text search tool Textpresso updated
SGD’s instance of Textpresso has recently been updated! Each week, SGD biocurators triage new publications from PubMed to load the newest yeast papers into the database. Once they are in SGD, those papers get indexed and loaded into Textpresso – a tool for full-text mining and searching. This is the new part: Content updates in SGD’s Textpresso are now happening on a weekly basis, meaning you can search full text of the very latest yeast papers!
You already love Textpresso for searching full text and its other bells and whistles:
- Search results shown in the context of the full text – hits to query terms highlighted in situ
- Custom corpus creation – you can decide which papers to search
- Search using Boolean operators
- Search scope options for document or sentence
- Search location options can constrain to specific sections of papers
Textpresso can be accessed via the “Full-text Search” link under “Literature” in the purple toolbar that runs across the top of most SGD webpages. Now you can search full text of the very latest yeast papers each week!
Biochemical Pathways now in SGD Search
YeastPathways, which is the database of metabolic pathways and enzymes in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is manually curated and maintained by the curation team at SGD.
This resource is jam-packed with information, but somewhat hidden from view. To make the pathways more readily accessible, some time ago we added a new section with pathways links on the relevant gene pages. Now the pathways are available in SGD Search!
The category “Biochemical Pathways” is now available, with facets (i.e., subcategories) for References and Loci. For even easier access, we also added the Pathway names and IDs to the autocomplete in the Search box, to enable quick browsing. Enjoy!
microPublications - latest yeast papers
microPublication Biology is part of the emerging genre of rapidly-published research communications. We are seeing a strong set of microPublications come through the database and are glad for this venue to publish brief, novel findings, negative and/or reproduced results, and results which may initially lack a broader scientific narrative. Each article is peer-reviewed, assigned a DOI, and indexed through PubMed and PubMedCentral.
Consider microPubublications when you have a result that doesn't necessarily fit into a larger story, but will be of value to others.
Latest yeast microPublications:
- Bennett SA, Cobos SN, Son E, Segal R, Mathew S, Yousuf H, Torrente MP (2023) Impaired RNA Binding Does Not Prevent Histone Modification Changes in a FUS ALS/FTD Yeast Model. MicroPubl Biol 2023
- Chang S, Joyson M, Kelly A, Tang L, Iannotta J, Rich A, Castilho Coelho N, Carvunis AR (2023) Unannotated Open Reading Frame in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Encodes Protein Localizing to the Endoplasmic Reticulum. MicroPubl Biol 2023
- Chen A, Gibney PA (2023) Disruption of GRR1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae rescues tps1Δ growth on fermentable carbon sources. MicroPubl Biol 2023
- Courtin B, Namane A, Gomard M, Meyer L, Jacquier A, Fromont-Racine M (2023) Xrn1 biochemically associates with eisosome proteins after the post diauxic shift in yeast. MicroPubl Biol 2023
- Delorme-Axford E, Tasmi TA, Klionsky DJ (2023) The Pho23-Rpd3 histone deacetylase complex regulates the yeast metabolic transcription factor Stb5. MicroPubl Biol 2023
- Garcia B, Riley KJ (2023) Saccharomyces cerevisiae NRE1 and IRC24 Encode Paralogous Benzil Oxidoreductases. MicroPubl Biol 2023
- Kowaleski SJ, Hurmis CS, Coleman CN, Philips KD, Najor NA (2023) SHE9 deletion mutants display fitness defects during diauxic shift in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . MicroPubl Biol 2023
- Runnebohm AM, Indovina CJ, Turk SM, Bailey CG, Orchard CJ, Wade L, Overton DL, Snow BJ, Rubenstein EM (2023) Methionine Restriction Impairs Degradation of a Protein that Aberrantly Engages the Endoplasmic Reticulum Translocon. MicroPubl Biol 2023
All yeast microPublications can be found in SGD.
Updates to SGD's YeastMine data warehouse
Allele SGDIDs added to YeastMine
YeastMine is SGD’s data warehouse, powered by InterMine. We have so many templates (i.e., pre-defined queries) that provide access to so many different kinds of data.
A big area of focus for SGD and the yeast community is alleles. Alleles are different versions of genes that vary in DNA and sometimes protein sequence. Did you know that you can easily and quickly get all curated yeast allele data directly from YeastMine?
The Genes -> Alleles template returns data for one gene or a list of genes or the entire genome! Data include standard and systematic names for genes, gene name descriptions, allele names and descriptions, allele types, aliases, and references. SGDIDs for genes are included, and now SGDIDs for the alleles have been added. Previously, this query returned all of these data without the SGDIDs for the alleles. Based on user feedback, we have now made these allele SGDIDs available, so that they can be used to identify and distinguish different alleles.
Downloads files added to YeastMine
Back in the day, SGD maintained an FTP site to distribute data in various files. More recently, you have found these files in the SGD Downloads site. We have now moved these files to YeastMine:
From the YeastMine homepage, click Templates at top left. In the Filter, select ‘Downloads’ to constrain the list of templates.
The following query templates are listed under Downloads:
- Deleted Merged Features: Retrieve all deleted and merged features.
- Retrieve Functional Complementation for genes: For gene(s), retrieve information about cross-species functional complementation between yeast and another species.
- Retrieve GO Terms: Retrieve GO Terms, including name, ID, namespace, and definition.
- Retrieve SGD chromosomal Features: Retrieve genes and other chromosomal features, including IDs, coordinates, and descriptions.
- Retrieve all cross-references for all genes: Retrieve IDs for yeast gene and gene products in other databases.
- Retrieve all domains of all genes: Retrieve Proteins/Genes that have a given domain.
- Retrieve all interactions for all genes: Retrieve physical and genetic interactions for all genes.
- Retrieve all pathways for all genes: Retrieve all metabolic pathways for all genes.
- Retrieve protein properties of all proteins of ORFs: Retrieve protein properties, including pI, molecular weight, N-terminal and C-terminal sequences, codon bias, etc. of all proteins.
For help using YeastMine, please see the SGD Help Pages and our YeastMine playlist on the SGD YouTube Channel.
Chemical structures now on Chemical pages in SGD
SGD curators use the Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) Ontology, maintained by EMBL-EBI, to describe chemicals used in experiments curated from yeast publications and displayed on SGD webpages.
You may have noticed that we have recently added chemical structures provided by ChEBI to the Chemical pages in SGD! Click the structure to zoom in, click again to zoom back out.
It’s a small detail, but we love this feature, and hope that you do too! Thanks, ChEBI!
Alliance of Genome Resources - Release 6.0
The Alliance of Genome Resources, a collaborative effort between SGD and other model organism databases (MOD), released version 6.0 in September 2023.
Version 6.0 adds new features to gene pages:
- New Paralogy section. Similar to Orthology, the Paralogy data are sourced from the DRSC’s DIOPT tool, which lets you view predictions from several tools at one time. Each table is ranked based on similarity, identity, alignment length, and a count of algorithms (methods) used to predict a paralogous match. See human HSPA1A gene page for an example.
- New Sequence Detail section. For different transcripts of the gene, you can choose to view the sequence for the gene, or its CDS, cDNA, protein, gene with collapsed introns, or genomic sequence with or without 500 bp up and downstream.
- Disease Qualifier. The qualifier describes whether a gene may be, for example, a marker_for the onset of a disease, or implicated_in the severity of a disease.
- Disease “Annotation details”. The pop-up for individual table rows has expanded to include Association, Additional Implicated Genes, Genetic Modifiers, Strain Background, Genetic Sex, Notes, and Annotation Type.
- The Download file from the gene page disease table now includes fields for Additional Implicated Gene ID, Additional Implicated Gene Symbol, Gene Association, Genetic Entity Association, Disease Qualifier, Evidence Code Abbreviation, Experimental Conditions, Genetic Modifier Relation, Genetic Modifier IDs, Genetic Modifier Names, Strain Background ID, Strain Background Name, Genetic Sex, Notes, Annotation Type, and Source URL.
- The Source column entries now link back to their respective resource webpages.
SGD's Social Media Footprint is Expanding
Discourse, Mastodon, BlueSky - oh my! Social media is in a chaotic period, with once tight-knit communities having been dismantled and thrown into the ether. SGD feels your pain; we have been searching for our audience, waiting for the stardust to settle, coagulate, coalesce.... In the interim, in an effort to reach you, we have set up SGD outposts on various platforms:
Discourse: The Alliance of Genome Resources Community Forum brings together communities of the major model organisms - yeast, worm, fly, zebrafish, frog, rat, and mouse - in one place. Users can create accounts to post announcements and questions, and chat with other researchers in a science-focused arena. Contact SGD for an invited account, which has additional permissions.
Mastodon: We're just getting started with Mastodon; follow SGD at @yeastgenome@genomic.social
BlueSky: We've also just begun with BlueSky; follow SGD at @yeastgenome.bsky.social
We will be cross-posting to the various accounts - come find SGD on these platforms and we can navigate this latest social media adventure together!
Upcoming Conferences and Courses
- TAGC2024 The Allied Genetics Conference
- National Harbor | Washington DC Metro Area
- March 05 to March 10, 2024
- 32nd Fungal Genetics Conference
- Asilomar Conference Grounds, Pacific Grove, CA
- March 12 to March 17, 2024
- 16th Yeast Lipid Conference
- May 29 to May 31, 2024 -
- Saarland University, Homburg, Germany
- JCS2024: Diversity and Evolution in Cell Biology
- June 24 to June 27, 2024 -
- Montanya Hotel & Lodge, Catalonia, Spain
- 39th Small Meeting of Yeast Transporters and Energetics (SMYTE)
- August 28 to September 01, 2024 -
- University of York, York, United Kingdom
- ICY2024: 16th International Congress on Yeasts
- Cape Town International Convention Centre, Cape Town, South Africa
- September 29 to October 03, 2024
Happy Holidays from SGD!
We want to take this opportunity to wish you and your family, friends and lab mates the best during the upcoming holidays. Stanford University will be closed for two weeks starting December 21, reopening on January 4th, 2024. Although SGD staff members will be taking time off, the website will be up and running throughout the winter break, and we will resume responding to user requests and questions in the new year.