Difference between revisions of "UW-Stout/Hydrogen Peroxide SP22"
(→Calibration Protocol) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
# Vortex Yeast Strains | # Vortex Yeast Strains | ||
| − | # Create 50ul Hydrogen Peroxide | + | # Create 50ul Hydrogen Peroxide dilutions as required |
| − | # Mix | + | # Mix dilutions With 50ul yeast cultures |
| − | # Put | + | # Put individual wells to grow For 24 hours |
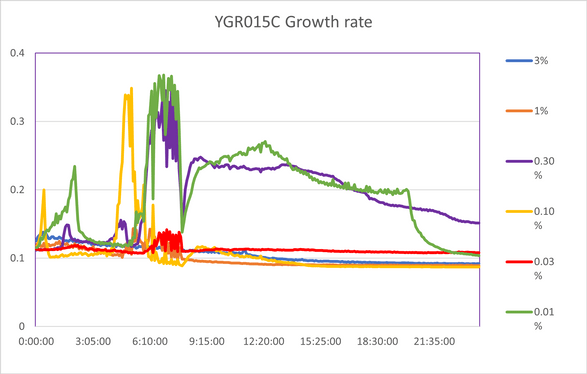
===Calibration Trial 1 Percent Series: 3%, 1%, 0.3%, 0.1%, 0.03%, 0.01%=== | ===Calibration Trial 1 Percent Series: 3%, 1%, 0.3%, 0.1%, 0.03%, 0.01%=== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
===Interpretation=== | ===Interpretation=== | ||
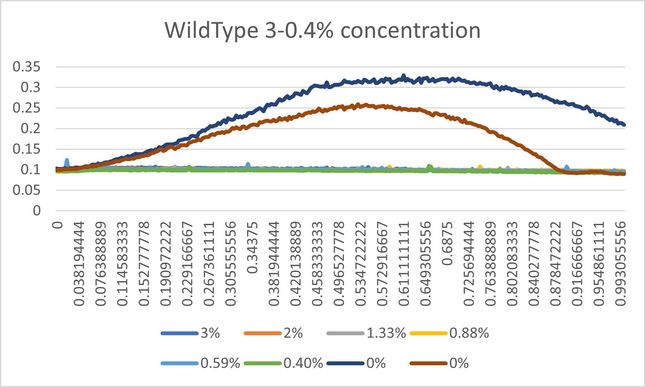
Based on both calibration experiments, we determined that the concentration of hydrogen peroxide tested on the yeast would need to be much lower if we wanted to see consistent amounts of inhibition and compare them. The higher concentrations in calibration 2 yielded data was too close among the knockout strains, so based on calibration 1 we settled on a dilution of 0.065%, as the range of 0.03% to 0.1% seemed to show the most observable differences in data. | Based on both calibration experiments, we determined that the concentration of hydrogen peroxide tested on the yeast would need to be much lower if we wanted to see consistent amounts of inhibition and compare them. The higher concentrations in calibration 2 yielded data was too close among the knockout strains, so based on calibration 1 we settled on a dilution of 0.065%, as the range of 0.03% to 0.1% seemed to show the most observable differences in data. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Knockout Protocol== | ||
| + | # Vortex Yeast Strains | ||
| + | # Create 50ul Hydrogen Peroxide dilutions as required | ||
| + | # Mix dilutions With 50ul yeast cultures | ||
| + | # Put in individual wells to grow For 24 hours | ||
| + | # Place standard controls in each well to growth for 24 hours as comparison | ||
| + | # Plot growth data. | ||
Revision as of 18:44, 4 May 2022
Contents
Introduction
Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) is a very strong oxidizer and antiseptic that is often used in dilute forms. The overall compound is found in biological systems but is in short lived reactions due to it's high toxicity over time. The goal of our experiment was to test how multiple yeast strains with knockout genes would respond in the presence of varying concentrations of hydrogen peroxide.
Materials
- Hydrogen Peroxide Solution 3% Concentration
- Distilled water for dilutions
- Wild Type and Knockout Yeast Strains
Equipment
- P-200 Micropipette
- P-20 Micropipette
- P-10 Micropipette
- Centrifuge Tubes
- Yeast Test Well
Calibration Protocol
H2O2 Dilutions
- Vortex Yeast Strains
- Create 50ul Hydrogen Peroxide dilutions as required
- Mix dilutions With 50ul yeast cultures
- Put individual wells to grow For 24 hours
Calibration Trial 1 Percent Series: 3%, 1%, 0.3%, 0.1%, 0.03%, 0.01%
Calibration Trial 2 Percent Series: 3%, 2%, 1.33%, 0.88%, 0.59%, 0.40%
Interpretation
Based on both calibration experiments, we determined that the concentration of hydrogen peroxide tested on the yeast would need to be much lower if we wanted to see consistent amounts of inhibition and compare them. The higher concentrations in calibration 2 yielded data was too close among the knockout strains, so based on calibration 1 we settled on a dilution of 0.065%, as the range of 0.03% to 0.1% seemed to show the most observable differences in data.
Knockout Protocol
- Vortex Yeast Strains
- Create 50ul Hydrogen Peroxide dilutions as required
- Mix dilutions With 50ul yeast cultures
- Put in individual wells to grow For 24 hours
- Place standard controls in each well to growth for 24 hours as comparison
- Plot growth data.