Difference between revisions of "SGD Newsletter, Spring 2021"
Mjalexander (talk | contribs) (→Textpresso Update) |
|||
| (74 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
'''About this newsletter:''' <br> | '''About this newsletter:''' <br> | ||
| − | This is the | + | This is the Spring 2021 issue of the SGD newsletter. The goal of this newsletter is to inform our users about new features in SGD and to foster communication within the yeast community. You can view this [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/SGD_Newsletter,_Spring_2021 newsletter] as well as previous newsletters on our [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/SGD_Newsletter_Archives Community Wiki]. |
| − | You can | ||
| − | |||
==R64.3 Annotation Update== | ==R64.3 Annotation Update== | ||
SGD curators periodically update the chromosomal annotations of the ''S. cerevisiae'' Reference Genome, which is derived from strain [http://www.yeastgenome.org/strain/S288C/overview S288C]. | SGD curators periodically update the chromosomal annotations of the ''S. cerevisiae'' Reference Genome, which is derived from strain [http://www.yeastgenome.org/strain/S288C/overview S288C]. | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | The R64.3 annotation release included various updates and additions: | + | The R64.3 annotation release, dated 2021-04-21, included various updates and additions: |
*7 new ORFs: [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303806 OTO1/YGR227C-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303807 YHR052C-B], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303808 YHR054C-B], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303810 YJR107C-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303811 YKL104W-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303812 YLR379W-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303813 YMR008C-A] | *7 new ORFs: [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303806 OTO1/YGR227C-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303807 YHR052C-B], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303808 YHR054C-B], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303810 YJR107C-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303811 YKL104W-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303812 YLR379W-A], [https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000303813 YMR008C-A] | ||
| Line 22: | Line 20: | ||
Various sequence and annotation files are available on SGD's [http://sgd-archive.yeastgenome.org/sequence/S288C_reference/ Downloads] site. You can find more update details and read about the new systematic nomenclature system for noncoding RNA genes on the [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/Details_of_2021_Reference_Genome_Annotation_Update_R64.3#R64.3_Annotation_update_summary Details of 2021 Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.3] SGD Wiki page. | Various sequence and annotation files are available on SGD's [http://sgd-archive.yeastgenome.org/sequence/S288C_reference/ Downloads] site. You can find more update details and read about the new systematic nomenclature system for noncoding RNA genes on the [https://wiki.yeastgenome.org/index.php/Details_of_2021_Reference_Genome_Annotation_Update_R64.3#R64.3_Annotation_update_summary Details of 2021 Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.3] SGD Wiki page. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==New Homology Pages== | ||
| + | |||
| + | SGD is excited to introduce our new Homology Pages! These pages can be accessed by clicking on the Homology tab in the header of SGD gene pages, as seen below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The information displayed on the Homology Pages is divided into several sections: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Homologs: Information about known homologs for the gene of interest, such as the species of the homolog, the corresponding Gene ID from the Alliance of Genome Resources, and the name of the homolog. | ||
| + | *Functional Complementation: Data about cross-species functional complementation between yeast and other species, curated by SGD and the Princeton Protein Orthology Database (P-POD). | ||
| + | *Fungal Homologs: Curated homolog information for 24 additional species of fungi. View the species of the fungal homolog, the database source of the entry, and the Gene ID of the homolog from that database. | ||
| + | *External Identifiers: A list of external identifiers for the protein from various database sources. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[File:homology1.png|650px|left|Image: 650 pixels|link=https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000000364]] [[File:homology2.png|750px|Image: 650 pixels|link=https://www.yeastgenome.org/locus/S000000364/homology]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Functional Complementation Data Available on References Pages== | ||
| + | Functional Complementation annotations are now viewable on reference pages for which there is curatable functional complementation data. This information describes cross-species functional complementation between yeast and other species, and is curated by SGD and the [http://ppod.princeton.edu Princeton Protein Orthology Database] (P-POD). | ||
| − | |||
| + | [[File:functional_comp3.png|600px|center|upright=0.8|link=https://www.yeastgenome.org/reference/S000274440]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
==YeastMine Updates and New Templates== | ==YeastMine Updates and New Templates== | ||
| − | + | SGD has updated the current [https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Gene_UTRs&scope=all Gene-->UTRs] YeastMine template with newly calculated 5' and 3' UTR sequence/coordinates. Additionally, transcript iso-forms for specific genes from the [http://www.yeastgenome.org/reference/S000153368/overview Pelachano et al., 2013] study can be accessed in YeastMine using the new [https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Gene_Transcript&scope=all Gene-->Transcripts] template. Both templates can be found under the "Templates" section of YeastMine under the "Expression" category. | |
| − | + | [[File:ym_templates.png|600px|center|upright=0.8|Transcript and UTR YeastMine Templates|link=https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/templates.do]] | |
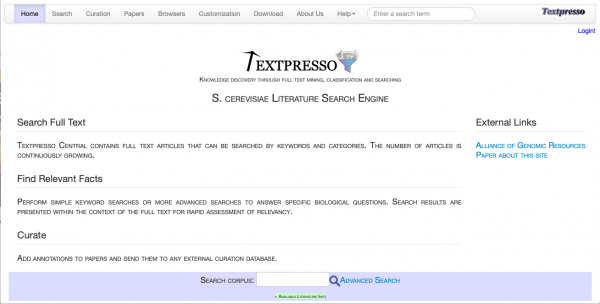
==Textpresso Central Update== | ==Textpresso Central Update== | ||
| − | [[File:textpresso.png|600px|left|upright=0.8|Textpresso | + | [[File:textpresso.png|600px|thumb|left|upright=0.8|Textpresso Central homepage|link=https://textpresso.yeastgenome.org/tpc/home]] |
| − | [https://textpresso.yeastgenome.org/tpc/home Textpresso] has recently been updated with a new system, adopting an overhauled user interface and introducing several new features | + | [https://textpresso.yeastgenome.org/tpc/home Textpresso] has recently been updated with a new system, adopting an overhauled user interface and introducing several new features including: |
| + | *Search results shown in the context of the full text | ||
| + | *Custom corpus creation | ||
| + | *Customizable annotation interface | ||
| + | *Search terms are highlighted in full-text view | ||
| + | |||
| + | Textpresso Central can also be accessed by clicking on "Full-text Search" under the Literature pull-down menu on the home page of SGD. More information about the changes and types of papers stored in Textpresso can be found in their [https://textpresso.yeastgenome.org/tpc/aboutus About Us] help section or (from [https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12859-018-2103-8 Müller et al., 2018]). | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
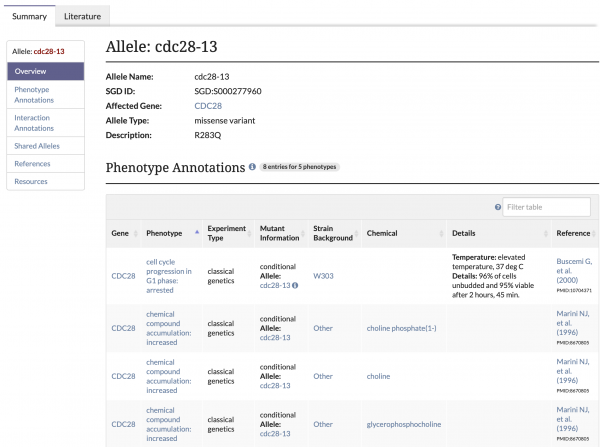
| − | + | ==Number of Curated Alleles Continues to Grow== | |
| + | SGD now has approximately '''13,000''' [https://www.yeastgenome.org/search?q=&category=allele alleles] that are either fully or partially curated. To navigate to an allele page, use the search bar to find a specific allele or enter a gene name and select an allele from the autocomplete list. Additionally, these pages can be accessed by clicking on the allele name in a gene’s Phenotype Annotation table. SGD Curators continue to add new alleles or update existing ones as new information becomes available. | ||
| − | + | You can generate a list of all alleles in our database or find alleles for a specific gene using the [https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/template.do?name=Gene_Alleles&scope=all Genes --> Alleles] template in [https://yeastmine.yeastgenome.org/yeastmine/begin.do YeastMine]. | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| − | + | [[File:allele_page.png|link=https://www.yeastgenome.org/allele/S000277751|600px|center|upright=.8]] | |
| − | + | <br> | |
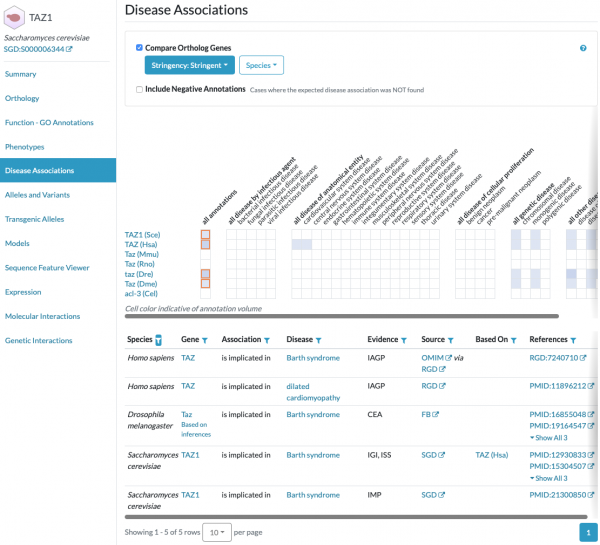
| − | [ | + | ==Alliance of Genome Resources - Disease Associations for model organisms== |
| + | Did you know that you can find human disease associations for yeast genes and their orthologs in other key model organisms at the [https://www.alliancegenome.org Alliance of Genome Resources]? | ||
| − | + | SGD is a founding member of the Alliance of Genome Resources, which was established to facilitate the use of diverse model organisms in understanding the genetic and genomic bases of human biology, health, and disease. [https://www.alliancegenome.org/gene/SGD:S000006344 Gene pages] for [https://www.alliancegenome.org/search?category=gene&species=Saccharomyces%20cerevisiae yeast] and [https://www.alliancegenome.org/search?category=gene other model organisms] at the Alliance include a section for Disease Associations, including those for orthologous genes. Human diseases are represented using the [https://disease-ontology.org Disease Ontology (DO)]. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:allianceDiseaseTAZ1.png|600px|center|upright=0.8|link=https://www.alliancegenome.org/gene/SGD:S000006344#disease-associations]] | |
| + | <br> | ||
| − | == | + | ==Fungal Pathogen Genomics Workshop== |
| − | [[File: | + | [[File:workshop.png|thumb|left|250px|link=https://coursesandconferences.wellcomeconnectingscience.org/event/fungal-pathogen-genomics-virtual-20210510/]] |
| + | From May 10th - 14th, Senior Biocuration Scientist Edith Wong, Senior Biocuration Scientist Rob Nash, Senior Biocuration Scientist Marek Skrzypek, Biocuration Scientist Suzi Aleksander, and Associate Biocuration Scientist Micheal Alexander were instructors for the [https://coursesandconferences.wellcomeconnectingscience.org/event/fungal-pathogen-genomics-virtual-20210510/ Virtual Fungal Pathogen Genomics Workshop] hosted by [https://coursesandconferences.wellcomeconnectingscience.org Wellcome Connecting Science]. Our curators helped attendees learn more about the unique tools hosted on our website and provided them the opportunity to learn about other curation tools from [https://veupathdb.org/veupathdb/app FungiDB], [https://fungi.ensembl.org/index.html EnsemblFungi], [http://www.candidagenome.org CGD], [https://mycocosm.jgi.doe.gov/mycocosm/home MycoCosm], and [https://genome.jgi.doe.gov/portal/ JGI]. | ||
| − | + | We would like to thank the Fungal Pathogen Genomics team for facilitating a successful virtual workshop, and for providing excellent training in web-based data mining resources for all attendees. | |
Latest revision as of 09:36, 14 December 2021
About this newsletter:
This is the Spring 2021 issue of the SGD newsletter. The goal of this newsletter is to inform our users about new features in SGD and to foster communication within the yeast community. You can view this newsletter as well as previous newsletters on our Community Wiki.
Contents
- 1 R64.3 Annotation Update
- 2 New Homology Pages
- 3 Functional Complementation Data Available on References Pages
- 4 YeastMine Updates and New Templates
- 5 Textpresso Central Update
- 6 Number of Curated Alleles Continues to Grow
- 7 Alliance of Genome Resources - Disease Associations for model organisms
- 8 Fungal Pathogen Genomics Workshop
R64.3 Annotation Update
SGD curators periodically update the chromosomal annotations of the S. cerevisiae Reference Genome, which is derived from strain S288C.
The R64.3 annotation release, dated 2021-04-21, included various updates and additions:
- 7 new ORFs: OTO1/YGR227C-A, YHR052C-B, YHR054C-B, YJR107C-A, YKL104W-A, YLR379W-A, YMR008C-A
- 5 new ncRNAs: GAL10-ncRNA, TBRT/XUT_2F-154, SUT169, PHO84 lncRNA, GAL4 lncRNA
- 2 new uORFs for ROK1/YGL171W
- 1 new recombination enhancer: RE
- 1 new LTR: YELWdelta27
- 3 ORFs with shifted translation starts: HPA3/YEL066W, YJR012C, LTO1/YNL260C
- 1 ORF with shifted translation stop plus new intron: LDO45/YMR147W
- Changed feature_type (and SO_term) for non-transcribed spacers: NTS1-2, NTS2-1, NTS2-2
- New systematic nomenclature system for entire annotated complement of ncRNAs
Various sequence and annotation files are available on SGD's Downloads site. You can find more update details and read about the new systematic nomenclature system for noncoding RNA genes on the Details of 2021 Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.3 SGD Wiki page.
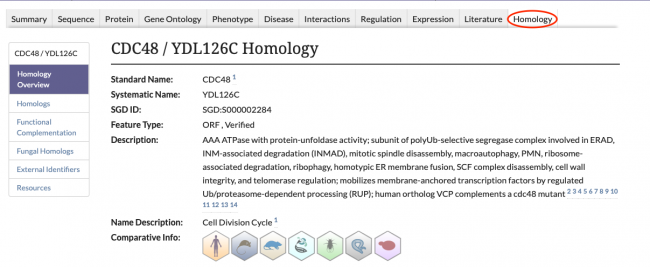
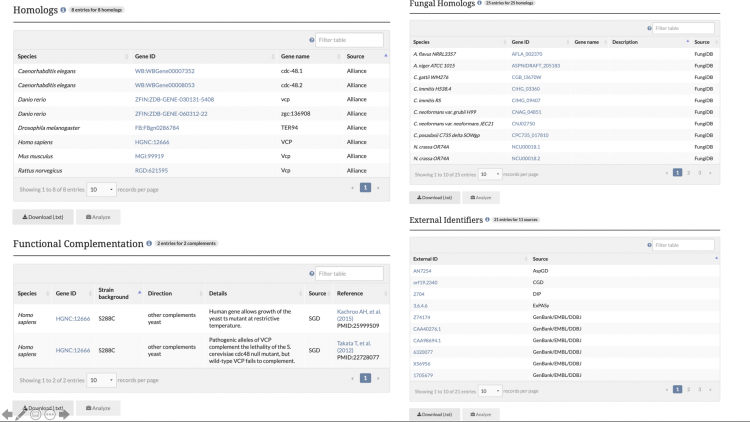
New Homology Pages
SGD is excited to introduce our new Homology Pages! These pages can be accessed by clicking on the Homology tab in the header of SGD gene pages, as seen below.
The information displayed on the Homology Pages is divided into several sections:
- Homologs: Information about known homologs for the gene of interest, such as the species of the homolog, the corresponding Gene ID from the Alliance of Genome Resources, and the name of the homolog.
- Functional Complementation: Data about cross-species functional complementation between yeast and other species, curated by SGD and the Princeton Protein Orthology Database (P-POD).
- Fungal Homologs: Curated homolog information for 24 additional species of fungi. View the species of the fungal homolog, the database source of the entry, and the Gene ID of the homolog from that database.
- External Identifiers: A list of external identifiers for the protein from various database sources.
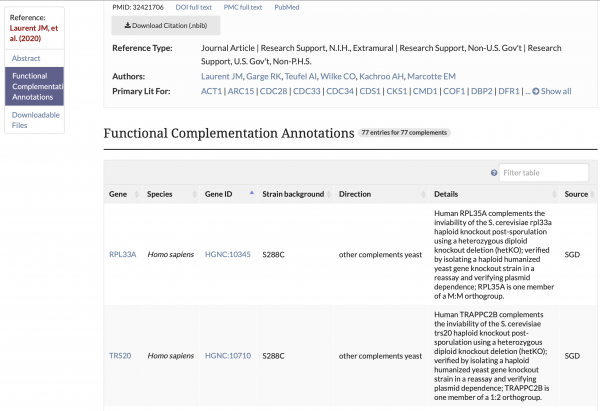
Functional Complementation Data Available on References Pages
Functional Complementation annotations are now viewable on reference pages for which there is curatable functional complementation data. This information describes cross-species functional complementation between yeast and other species, and is curated by SGD and the Princeton Protein Orthology Database (P-POD).
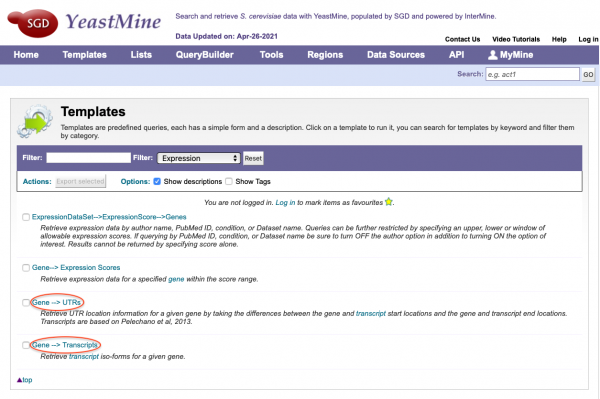
YeastMine Updates and New Templates
SGD has updated the current Gene-->UTRs YeastMine template with newly calculated 5' and 3' UTR sequence/coordinates. Additionally, transcript iso-forms for specific genes from the Pelachano et al., 2013 study can be accessed in YeastMine using the new Gene-->Transcripts template. Both templates can be found under the "Templates" section of YeastMine under the "Expression" category.
Textpresso Central Update
Textpresso has recently been updated with a new system, adopting an overhauled user interface and introducing several new features including:
- Search results shown in the context of the full text
- Custom corpus creation
- Customizable annotation interface
- Search terms are highlighted in full-text view
Textpresso Central can also be accessed by clicking on "Full-text Search" under the Literature pull-down menu on the home page of SGD. More information about the changes and types of papers stored in Textpresso can be found in their About Us help section or (from Müller et al., 2018).
Number of Curated Alleles Continues to Grow
SGD now has approximately 13,000 alleles that are either fully or partially curated. To navigate to an allele page, use the search bar to find a specific allele or enter a gene name and select an allele from the autocomplete list. Additionally, these pages can be accessed by clicking on the allele name in a gene’s Phenotype Annotation table. SGD Curators continue to add new alleles or update existing ones as new information becomes available.
You can generate a list of all alleles in our database or find alleles for a specific gene using the Genes --> Alleles template in YeastMine.
Alliance of Genome Resources - Disease Associations for model organisms
Did you know that you can find human disease associations for yeast genes and their orthologs in other key model organisms at the Alliance of Genome Resources?
SGD is a founding member of the Alliance of Genome Resources, which was established to facilitate the use of diverse model organisms in understanding the genetic and genomic bases of human biology, health, and disease. Gene pages for yeast and other model organisms at the Alliance include a section for Disease Associations, including those for orthologous genes. Human diseases are represented using the Disease Ontology (DO).
Fungal Pathogen Genomics Workshop
From May 10th - 14th, Senior Biocuration Scientist Edith Wong, Senior Biocuration Scientist Rob Nash, Senior Biocuration Scientist Marek Skrzypek, Biocuration Scientist Suzi Aleksander, and Associate Biocuration Scientist Micheal Alexander were instructors for the Virtual Fungal Pathogen Genomics Workshop hosted by Wellcome Connecting Science. Our curators helped attendees learn more about the unique tools hosted on our website and provided them the opportunity to learn about other curation tools from FungiDB, EnsemblFungi, CGD, MycoCosm, and JGI.
We would like to thank the Fungal Pathogen Genomics team for facilitating a successful virtual workshop, and for providing excellent training in web-based data mining resources for all attendees.